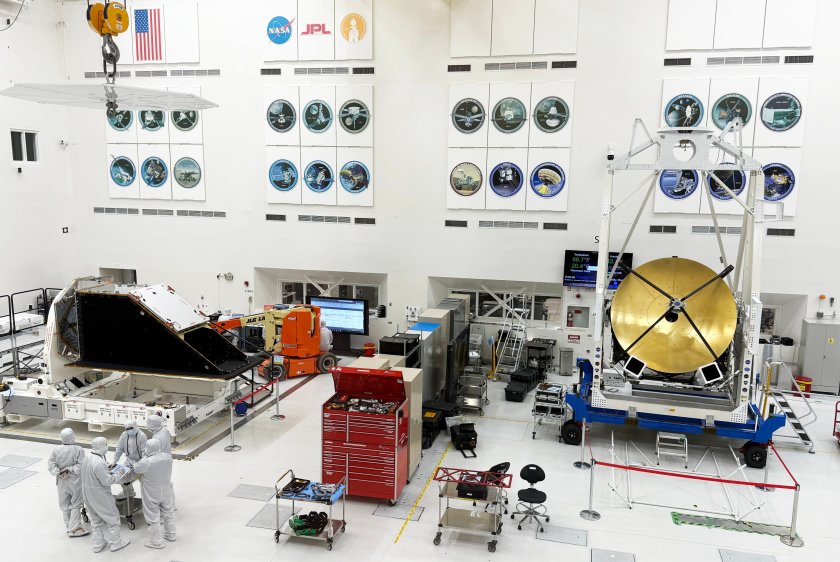
Work on NASA’s purpose-built asteroid hunter, Near-Earth Object (NEO) Surveyor, is progressing toward a targeted late 2027 launch. A major component of the mission, the spacecraft’s instrument enclosure journeyed back to the agency’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California in early March after completing environmental testing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston.
Built at JPL, the angular 12-foot-long (3.7-meter-long) structure will protect the spacecraft’s infrared telescope and remove heat from it during space operations. Infrared telescopes essentially detect heat, so they need to be kept cool to avoid heat from the spacecraft interfering with observations.
As NASA’s first space-based detection mission specifically designed for planetary defense, NEO Surveyor is sensitive to the heat emitted by near-Earth objects that are warmed by the Sun, allowing it to spot even those with dark surfaces. The observatory will use its infrared capabilities to detect and characterize the hardest-to-find asteroids and comets that might pose an impact hazard to Earth.
Over the course of several weeks at JPL, engineers and technicians will reinstall cables and finish taping the edges of the instrument enclosure’s composite panels in the historic High Bay 1 clean room of the lab’s Spacecraft Assembly Facility. The work is viewable via a live camera feed. Sharing the room with NEO Surveyor’s hardware is the telescope for NASA’s ASTHROS (Astrophysics Stratospheric Telescope for High Spectral Resolution Observations at Submillimeter-wavelengths), an atmospheric balloon mission.
Once work wraps up on NEO Surveyor’s instrument enclosure, it’ll be sent to the Space Dynamics Laboratory (SDL) in Logan, Utah, where it will be joined together with another piece of key hardware: the telescope’s aluminum body, called the optical telescope assembly, which JPL also built. The telescope itself already left JPL earlier in the month, arriving at SDL on March 13.
The NEO Surveyor mission is led by Professor Amy Mainzer at UCLA for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office and is being managed by JPL for the Planetary Missions Program Office at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. BAE Systems, SDL, and Teledyne are among the companies that were contracted to build the spacecraft and its instrumentation. The Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics at the University of Colorado Boulder will support operations, and Caltech’s IPAC in Pasadena, California, is responsible for producing some of the mission’s data products. Caltech manages JPL for NASA.
More information about NEO Surveyor is available at: