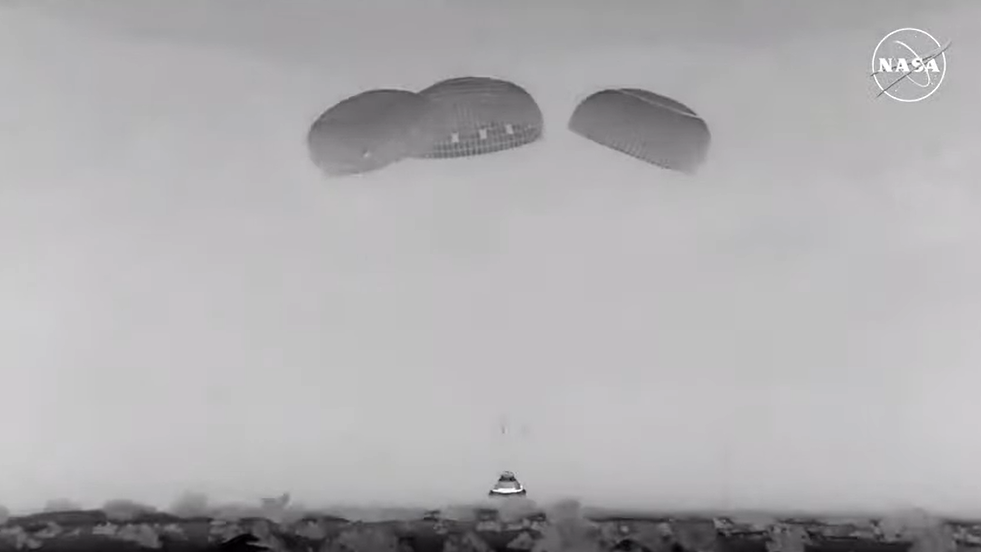
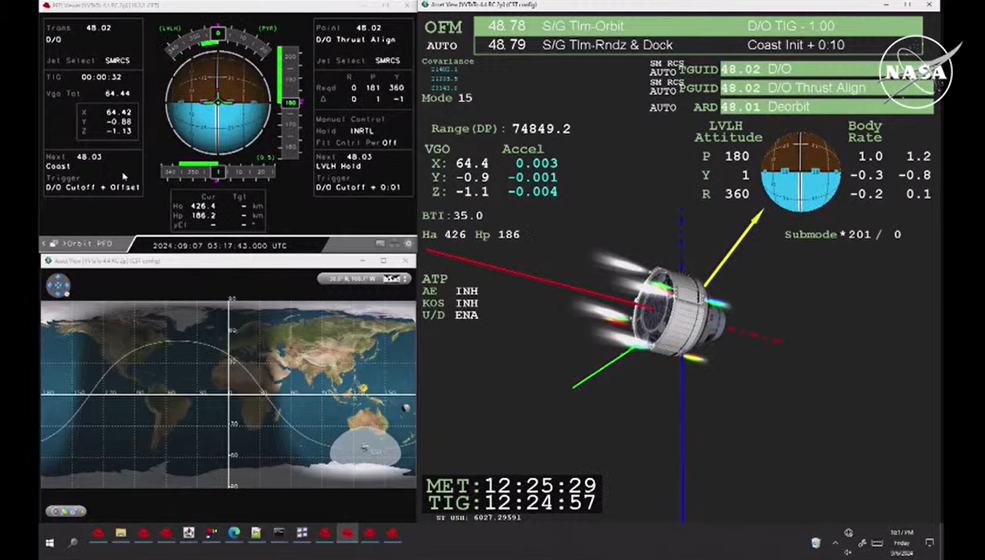
At 12:01 a.m. EDT, Boeing’s uncrewed Starliner spacecraft landed at White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico.
NASA will provide coverage of a post-landing news conference at 1:30 a.m. on NASA+, the NASA app, YouTube, and the agency’s website.
The following will participate in the news conference:
- Joel Montalbano, deputy associate administrator, Space Operations Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters in Washington
- Steve Stich, manager, Commercial Crew Program, NASA Kennedy Space Center in Florida
- Dana Weigel, manager, International Space Station, NASA Johnson
Learn more about the mission by following the commercial crew blog, @commercial_crew on X, and @NASACommercialCrew on Facebook.