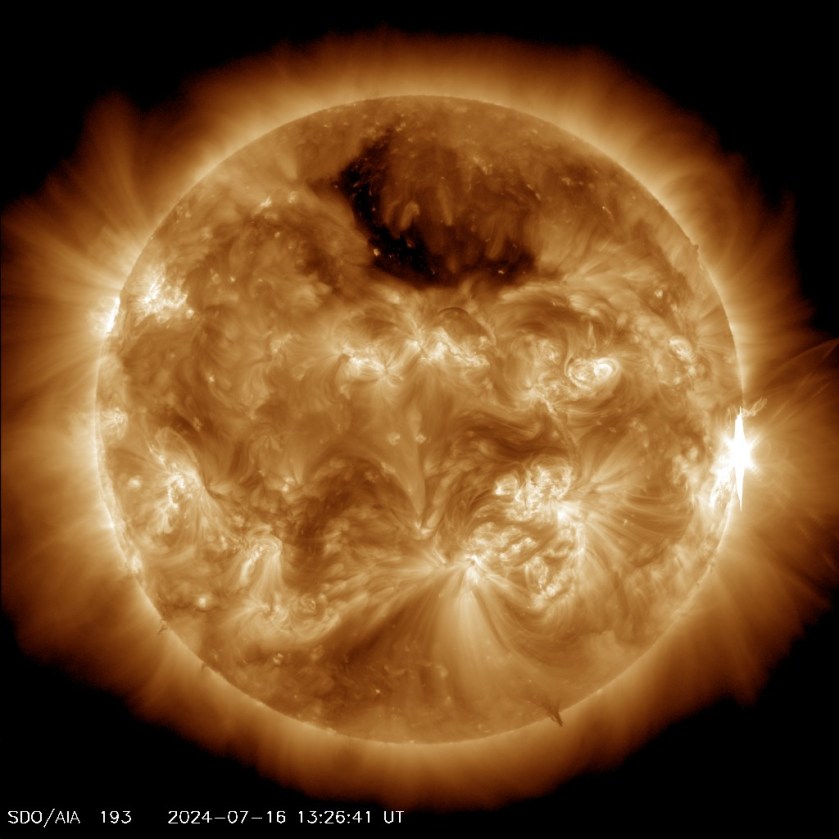
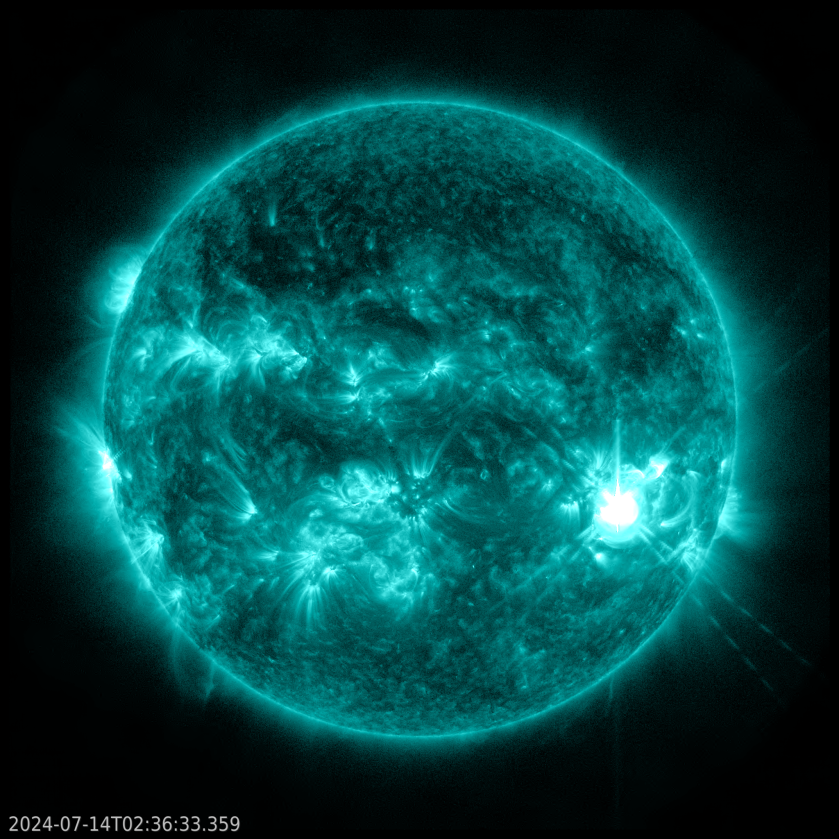
The Sun emitted a strong solar flare, peaking at 10:37 p.m. on July 28, 2024. NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory, which watches the Sun constantly, captured an image of the event.
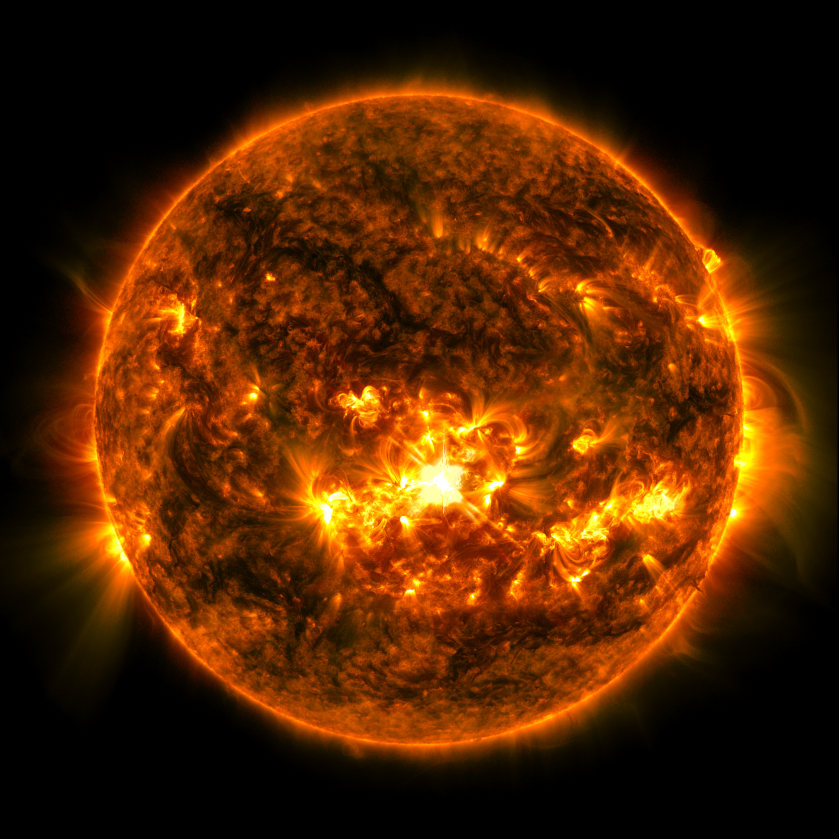

Solar flares are powerful bursts of energy. Flares and solar eruptions can impact radio communications, electric power grids, navigation signals, and pose risks to spacecraft and astronauts.
This flare is classified as an X1.5 flare. X-class denotes the most intense flares, while the number provides more information about its strength.
To see how such space weather may affect Earth, please visit NOAA’s Space Weather Prediction Center https://spaceweather.gov/, the U.S. government’s official source for space weather forecasts, watches, warnings, and alerts. NASA works as a research arm of the nation’s space weather effort. NASA observes the Sun and our space environment constantly with a fleet of spacecraft that study everything from the Sun’s activity to the solar atmosphere, and to the particles and magnetic fields in the space surrounding Earth.