With giant storms, powerful winds, auroras, and extreme temperature and pressure conditions, Jupiter has a lot going on. Now, NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has captured new images of the planet. Webb’s Jupiter observations will give scientists even more clues to Jupiter’s inner life.
“We hadn’t really expected it to be this good, to be honest,” said planetary astronomer Imke de Pater, professor emerita of the University of California, Berkeley. De Pater led the observations of Jupiter with Thierry Fouchet, a professor at the Paris Observatory, as part of an international collaboration for Webb’s Early Release Science program. Webb itself is an international mission led by NASA with its partners ESA (European Space Agency) and CSA (Canadian Space Agency). “It’s really remarkable that we can see details on Jupiter together with its rings, tiny satellites, and even galaxies in one image,” she said.
The two images come from the observatory’s Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam), which has three specialized infrared filters that showcase details of the planet. Since infrared light is invisible to the human eye, the light has been mapped onto the visible spectrum. Generally, the longest wavelengths appear redder and the shortest wavelengths are shown as more blue. Scientists collaborated with citizen scientist Judy Schmidt to translate the Webb data into images.
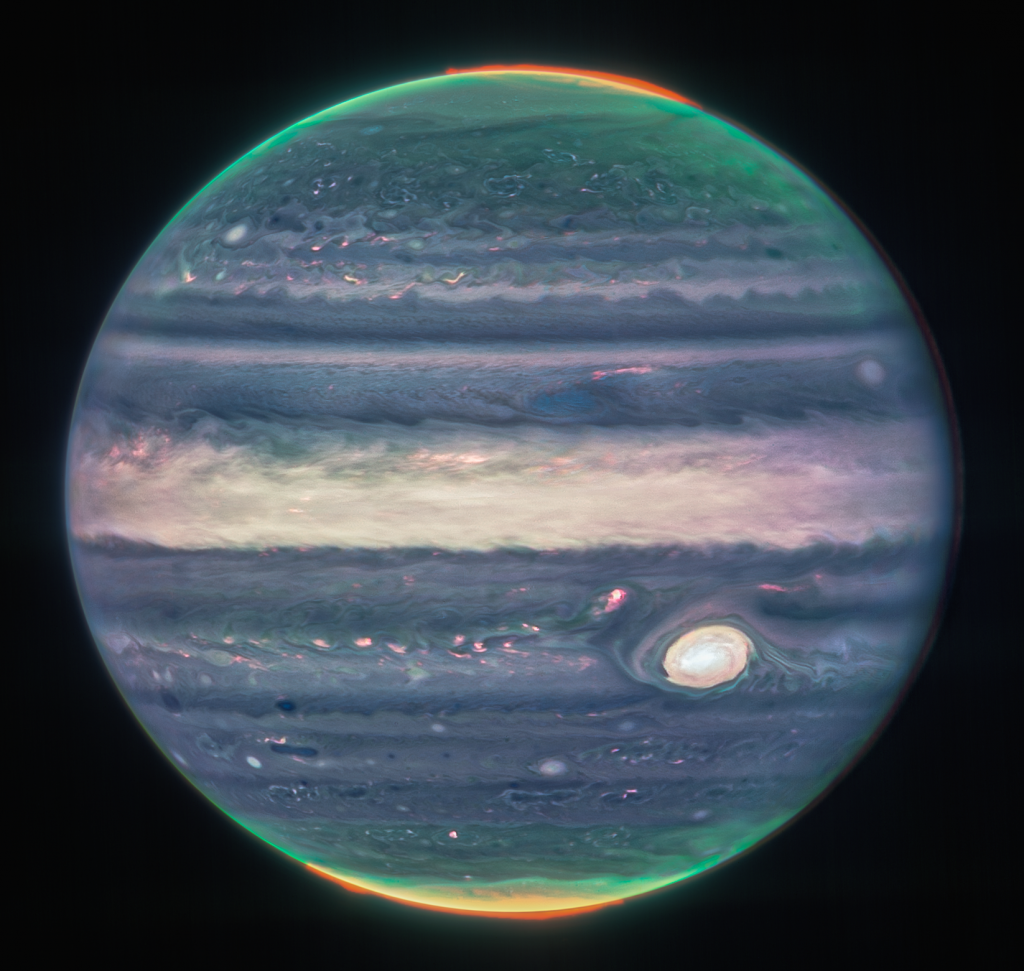
In the standalone view of Jupiter, created from a composite of several images from Webb, auroras extend to high altitudes above both the northern and southern poles of Jupiter. The auroras shine in a filter that is mapped to redder colors, which also highlights light reflected from lower clouds and upper hazes. A different filter, mapped to yellows and greens, shows hazes swirling around the northern and southern poles. A third filter, mapped to blues, showcases light that is reflected from a deeper main cloud.
The Great Red Spot, a famous storm so big it could swallow Earth, appears white in these views, as do other clouds, because they are reflecting a lot of sunlight.
“The brightness here indicates high altitude – so the Great Red Spot has high-altitude hazes, as does the equatorial region,” said Heidi Hammel, Webb interdisciplinary scientist for solar system observations and vice president for science at AURA. “The numerous bright white ‘spots’ and ‘streaks’ are likely very high-altitude cloud tops of condensed convective storms.” By contrast, dark ribbons north of the equatorial region have little cloud cover.
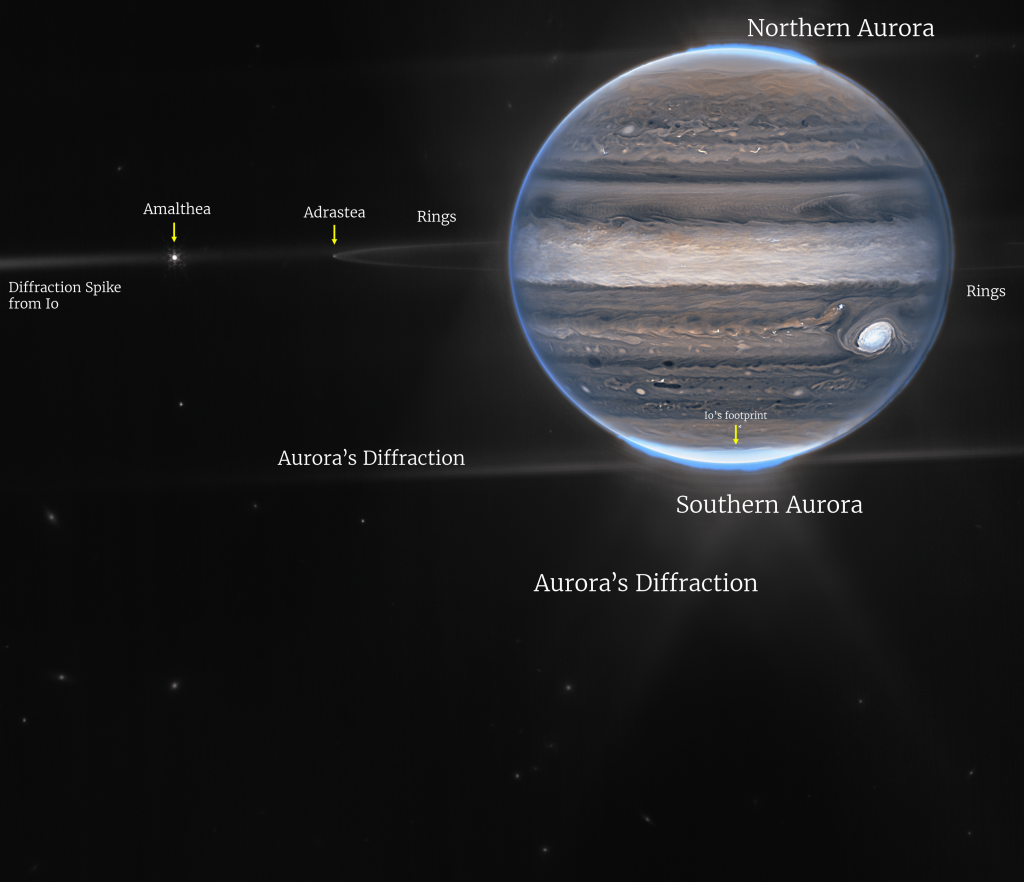
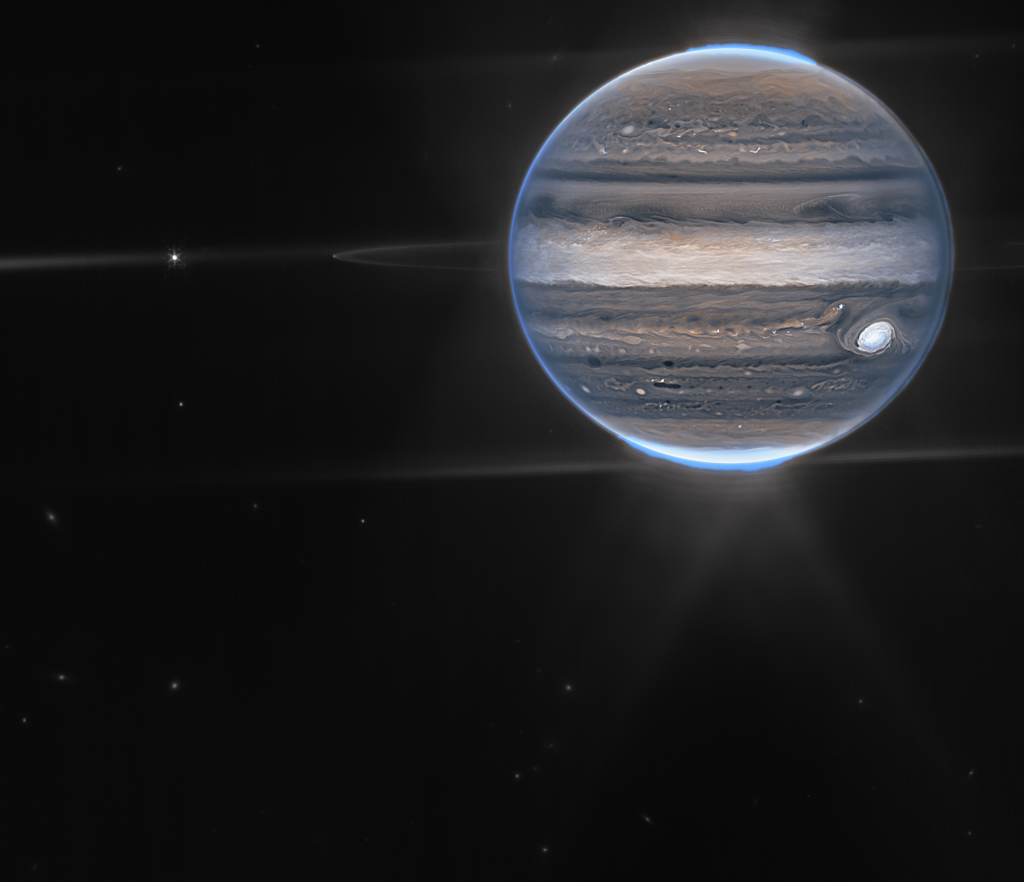
In a wide-field view, Webb sees Jupiter with its faint rings, which are a million times fainter than the planet, and two tiny moons called Amalthea and Adrastea. The fuzzy spots in the lower background are likely galaxies “photobombing” this Jovian view.
“This one image sums up the science of our Jupiter system program, which studies the dynamics and chemistry of Jupiter itself, its rings, and its satellite system,” Fouchet said. Researchers have already begun analyzing Webb data to get new science results about our solar system’s largest planet.
Data from telescopes like Webb doesn’t arrive on Earth neatly packaged. Instead, it contains information about the brightness of the light on Webb’s detectors. This information arrives at the Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI), Webb’s mission and science operations center, as raw data. STScI processes the data into calibrated files for scientific analysis and delivers it to the Mikulski Archive for Space Telescopes for dissemination. Scientists then translate that information into images like these during the course of their research (here’s a podcast about that). While a team at STScI formally processes Webb images for official release, non-professional astronomers known as citizen scientists often dive into the public data archive to retrieve and process images, too.
Judy Schmidt of Modesto California, a longtime image processor in the citizen science community, processed these new views of Jupiter. For the image that includes the tiny satellites, she collaborated with Ricardo Hueso, a co-investigator on these observations, who studies planetary atmospheres at the University of the Basque Country in Spain.
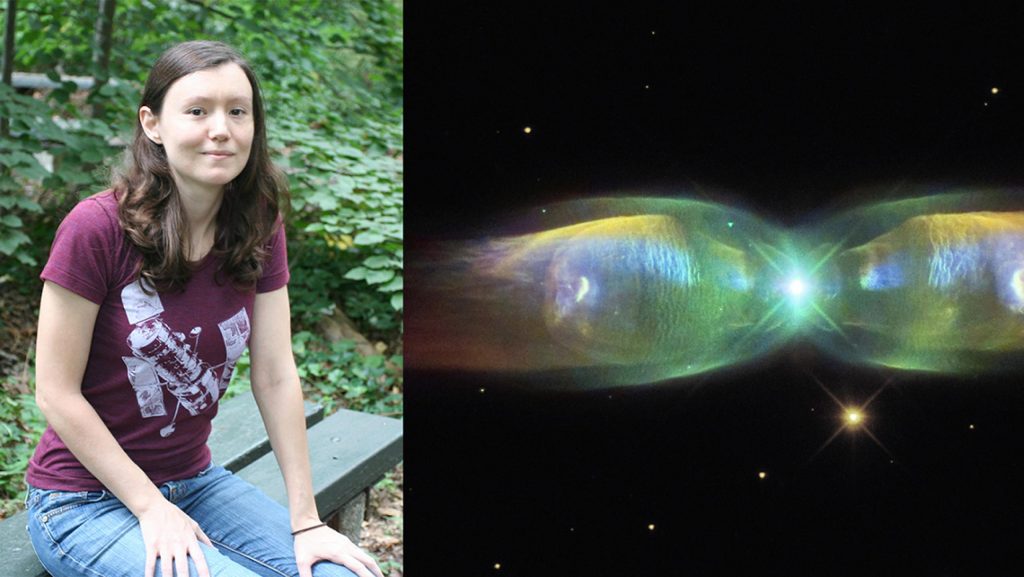

Schmidt has no formal educational background in astronomy. But 10 years ago, an ESA contest sparked her insatiable passion for image processing. The “Hubble’s Hidden Treasures” competition invited the public to find new gems in Hubble data. Out of nearly 3,000 submissions, Schmidt took home third place for an image of a newborn star.
Since the ESA contest, she has been working on Hubble and other telescope data as a hobby. “Something about it just stuck with me, and I can’t stop,” she said. “I could spend hours and hours every day.”
Her love of astronomy images led her to process images of nebulae, globular clusters, stellar nurseries, and more spectacular cosmic objects. Her guiding philosophy is: “I try to get it to look natural, even if it’s not anything close to what your eye can see.” These images have caught the attention of professional scientists, including Hammel, who previously collaborated with Schmidt on refining Hubble images of comet Shoemaker-Levy 9’s Jupiter impact.
Jupiter is actually harder to work with than more distant cosmic wonders, Schmidt says, because of how fast it rotates. Combining a stack of images into one view can be challenging when Jupiter’s distinctive features have rotated during the time that the images were taken and are no longer aligned. Sometimes she has to digitally make adjustments to stack the images in a way that makes sense.
Webb will deliver observations about every phase of cosmic history, but if Schmidt had to pick one thing to be excited about, it would be more Webb views of star-forming regions. In particular, she is fascinated by young stars that produce powerful jets in small nebula patches called Herbig–Haro objects. “I’m really looking forward to seeing these weird and wonderful baby stars blowing holes into nebulas,” she said.
– Elizabeth Landau, NASA Headquarters
To learn more about the Webb mission, visit nasa.gov/webb. For more information about NASA citizen science – and how you can get involved doing real NASA Science – go to science.nasa.gov/citizenscience.

