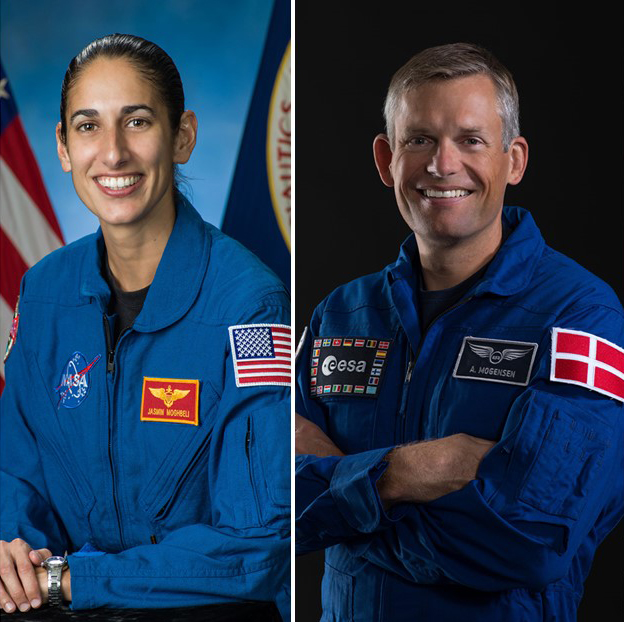
NASA and SpaceX are targeting mid-August for the launch of Crew-7, the next rotational mission to the International Space Station aboard a SpaceX Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
NASA astronaut Jasmin Moghbeli and ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Andreas Mogensen will serve as spacecraft commander and pilot, respectively, for the mission. Two mission specialists will be announced later, following review by NASA and its international partners. Moghbeli, Mogensen, and the additional mission specialists will join an expedition crew aboard the space station.
Crew Flight Test Targeting July 21
Launch of NASA’s Boeing Crew Flight Test (CFT) to the International Space Station is targeted for no earlier than Friday, July 21, pending coordination for the U.S. Eastern Range availability. The new target date provides NASA and Boeing the necessary time to complete subsystem verification testing and close out test flight certification products and aligns with the space station manifest and range launch opportunities.
Space Station Cargo, Research Work Ongoing
The Expedition 69 crew members continue unpacking the SpaceX Dragon resupply ship in the midst of human research and pharmaceutical studies aboard the International Space Station. NASA and its commercial crew partners have also announced upcoming missions to the station.
Flight Engineers Frank Rubio of NASA and Sultan Alneyadi of UAE (United Arab Emirates) took turns working inside the SpaceX Dragon cargo craft on Thursday. The duo has been offloading some of the 6,200 pounds new research gear and crew supplies packed inside the Cargo Dragon. The U.S. commercial space freighter will remain docked to the Harmony module’s forward port until mid-April when it will return to Earth filled with completed science experiments and other cargo for retrieval and analysis.
Rubio started his day pedaling on the station’s exercise bike while attached to sensors to measure his aerobic capacity in microgravity. Afterward, he performed research work in the Columbus laboratory module to understand how the different gravity levels of the Moon, Mars, and beyond may affect the biomanufacturing of pharmaceuticals.
Alneyadi’s first task of the day was to install an incubator in the Kibo laboratory module and later activate it in the afternoon. He also collected surface samples throughout the space station for microbial analysis back on Earth.
Station Commander Sergey Prokopyev was joined by Rubio and Roscosmos Flight Engineer Dmitri Petelin during the morning checking their Soyuz launch and entry suits for leaks. Prokopyev and Petelin then tested communications with the ISS Progress 83 cargo craft docked to the Zvezda service module’s rear port. Flight Engineer Andrey Fedyaev worked throughout Thursday on computer maintenance and orbital plumbing tasks.

