NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative soon will send two CubeSats to the International Space Station as cargo on the 21st Northrop Grumman commercial resupply mission.
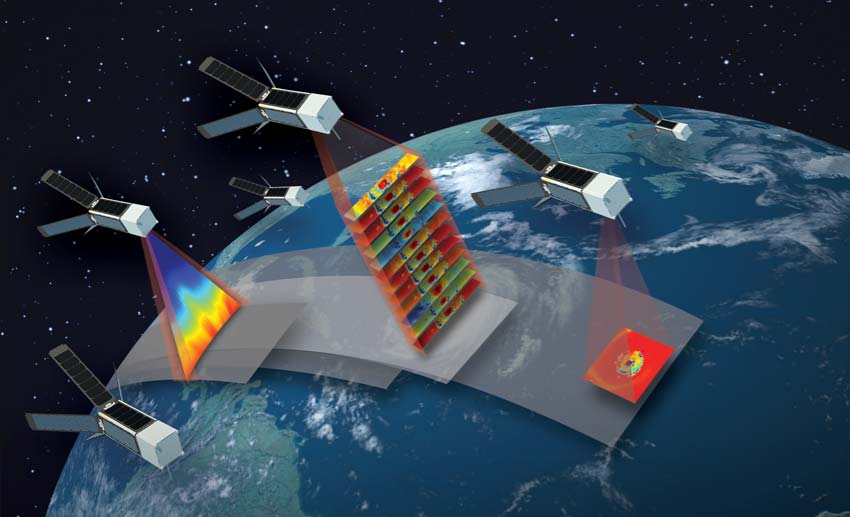
CySat-1, designed and built by students from Iowa State University, measures Earth’s soil moisture content from low Earth orbit. The measurements will be taken with a software-defined radiometer, a system that uses software to process analog radio signals. Students will create computer programs to analyze those signals to determine levels of moisture in the soil present on the Earth. As Iowa State University’s first CubeSat, CySat-1 will be a technology demonstrator for future CubeSat missions.
Students at Arizona State University and NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Southern California developed DORA (Deployable Optical Receiver Aperture), a new technology CubeSat.
In the past, small satellites required precision pointing and only achieved low data transmissions in gathering information. The technology will demonstrate new optical communications without precision pointing and use a solid-state photon detector to gather high data rates using wide-field optical receivers. To test the detector’s performance, DORA will measure the background light from reflected sunlight, moonlight, and city lights when deployed from the space station into low Earth orbit.
The two demonstrations, CySat-1 and DORA, are both 3U CubeSats, a class of small satellites. The cube-shaped spacecraft are sized in standardized units, or Us, typically up to 12U. One CubeSat unit is defined as a volume of about 10x10x10 cm in size and typically weighs less than 2 kilograms.
The satellites will be released from the International Space Station using the Nanoracks CubeSat Deployer. One of the space station’s arms grabs and points the deployer in the proper direction to release the CubeSats into orbit.
Launch of the Cygnus spacecraft is targeted at 11:28 a.m. EDT Saturday, Aug. 3, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.