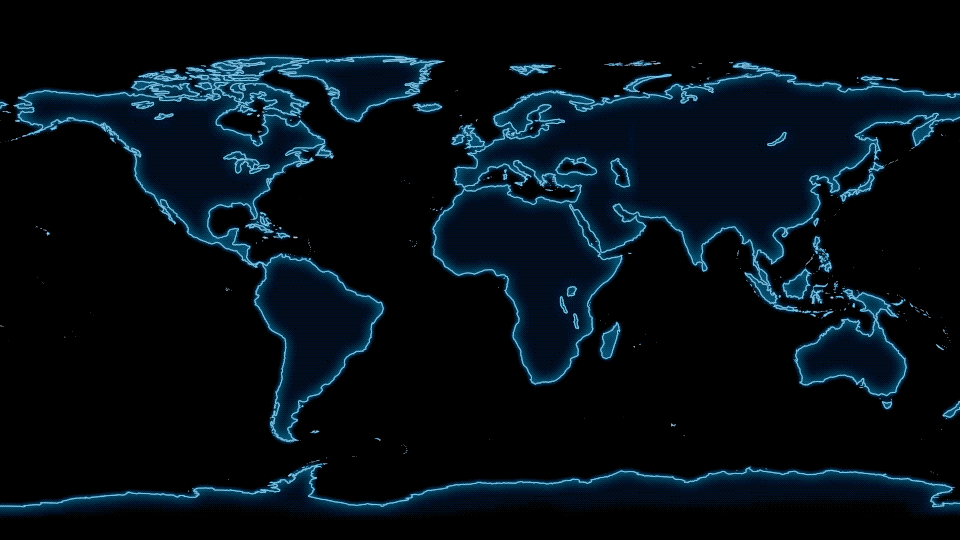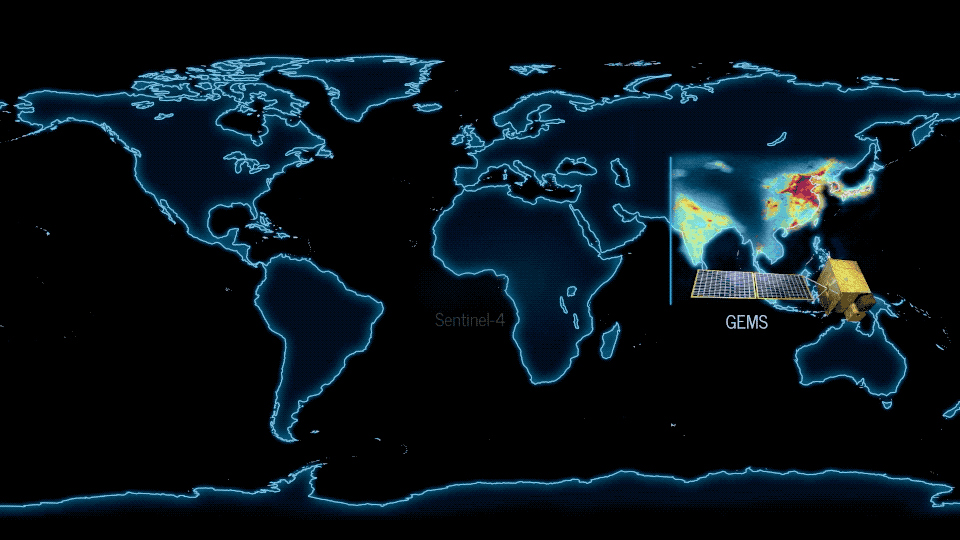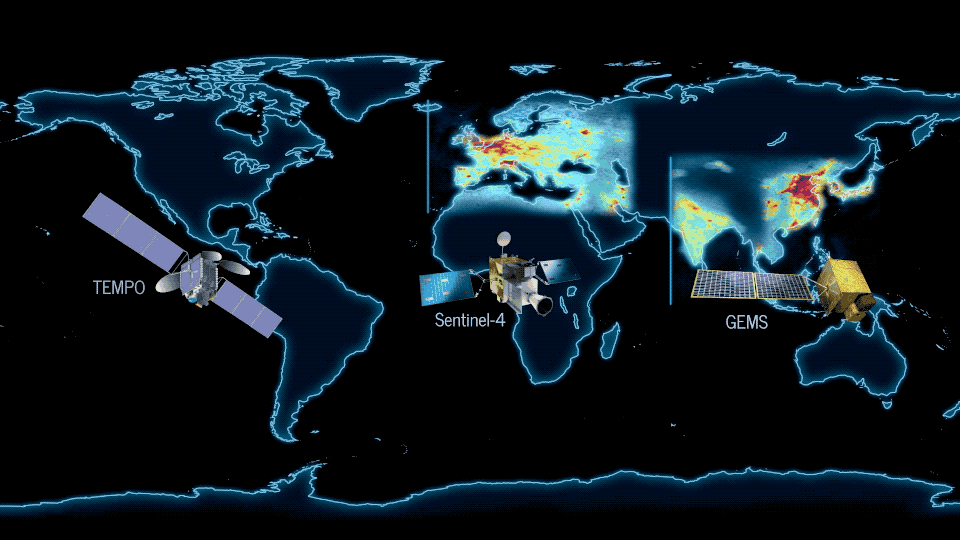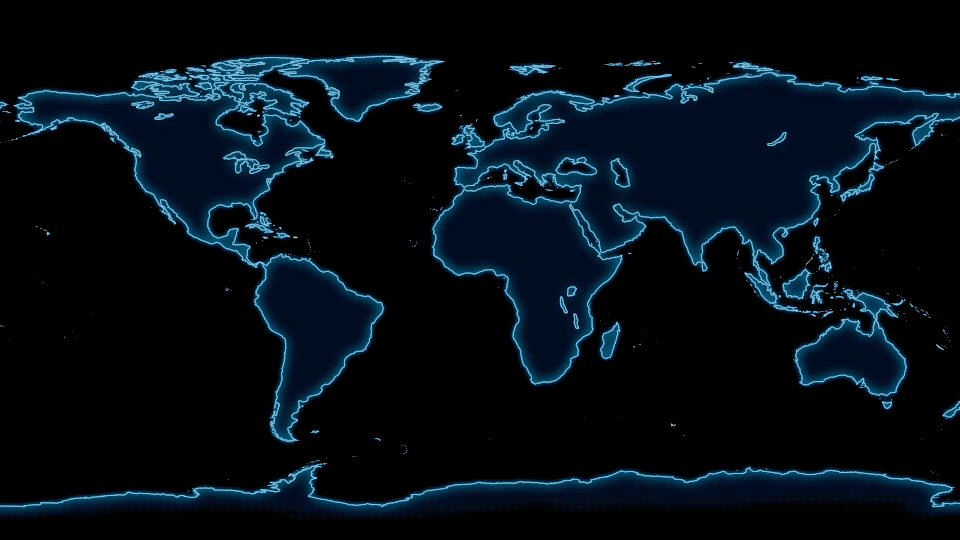
On Feb. 18 a new era began in an international effort to improve air quality science and forecasting around the world . The first of three instruments in a pioneering new space-based constellation launched from French Guiana to make hourly daytime measurements of several air pollutants.
South Korea’s Geostationary Environment Monitoring Spectrometer (GEMS) instrument rocketed into space on the Korean Aerospace Research Institute GEO-KOMPSAT-2B satellite. From a geostationary, or fixed, orbital location, GEMS will make measurements over Asia. NASA’s Tropospheric Emissions: Monitoring of Pollution (TEMPO), scheduled to launch in 2022, will make measurements over North America. To complete the constellation, the European Space Agency Sentinel-4 satellite, expected to launch in 2023, will make measurements over Europe and North Africa.
 Once complete, this air quality satellite “virtual constellation” will measure pollutants — including ozone, nitrogen dioxide, formaldehyde and tiny atmospheric particles called aerosols — in unprecedented detail and frequency. Air pollution can be damaging to the human respiratory and cardiovascular system and to the environment. Near-real-time data products from the constellation will significantly improve air quality forecasting around the most densely populated areas of the Northern Hemisphere. That data can also help inform decisions by policymakers to improve air quality.
Once complete, this air quality satellite “virtual constellation” will measure pollutants — including ozone, nitrogen dioxide, formaldehyde and tiny atmospheric particles called aerosols — in unprecedented detail and frequency. Air pollution can be damaging to the human respiratory and cardiovascular system and to the environment. Near-real-time data products from the constellation will significantly improve air quality forecasting around the most densely populated areas of the Northern Hemisphere. That data can also help inform decisions by policymakers to improve air quality.
