Engineers have initiated power up of the flight computes and avionics for the Artemis I core stage. This begins the countdown for the hot fire test with the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket scheduled for Thursday, March 18.
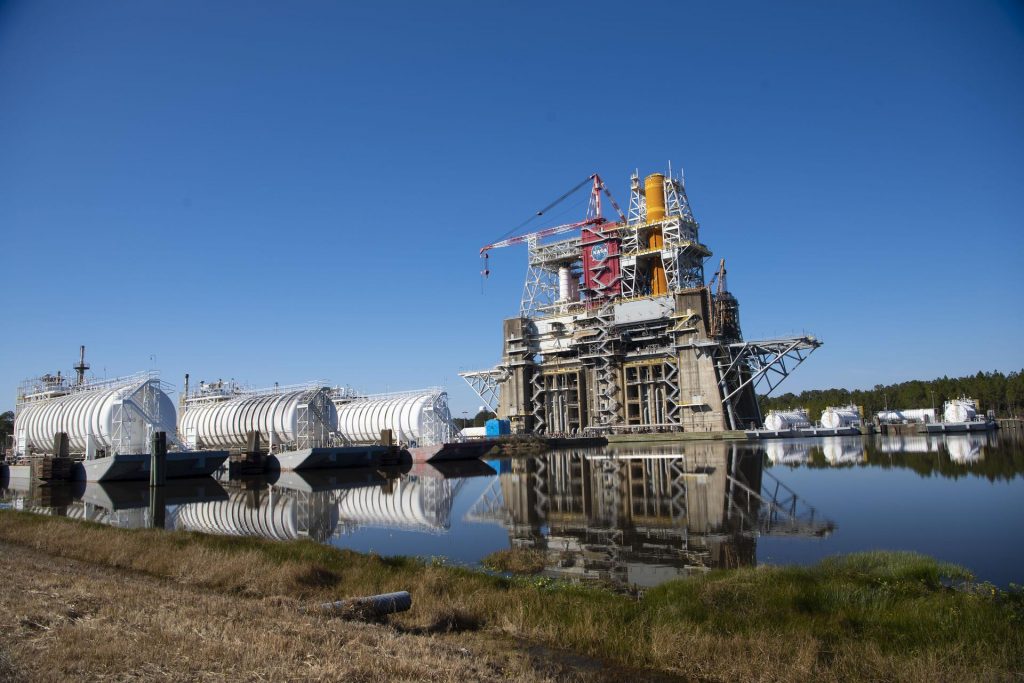
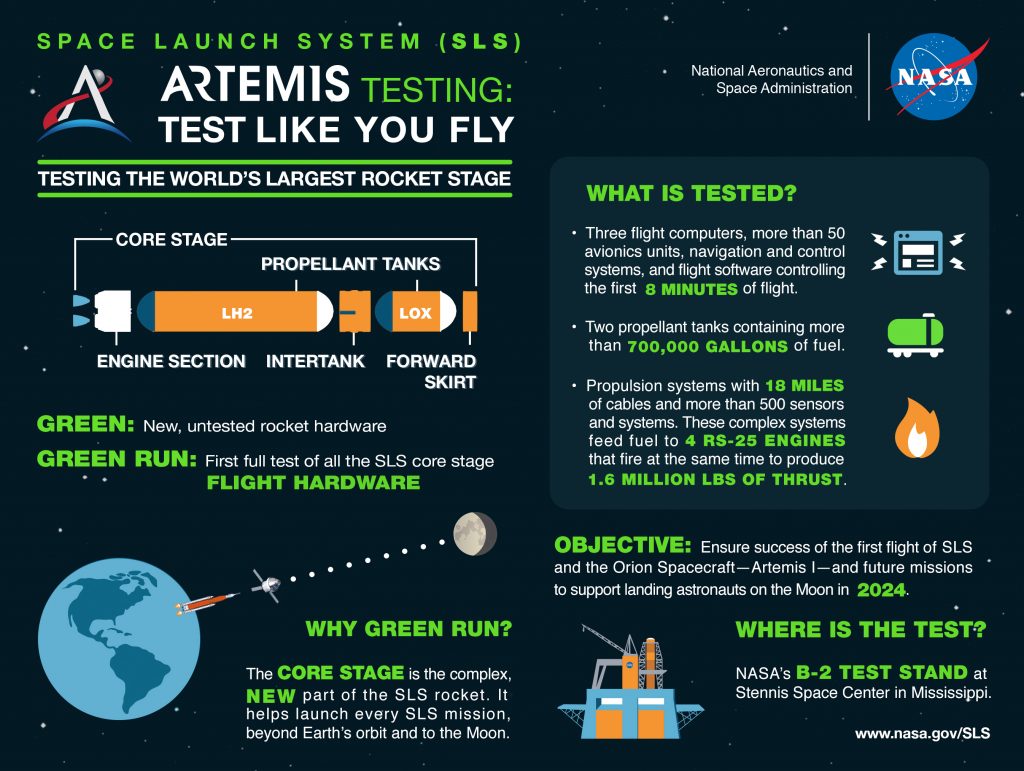
Before the test, the management team in the Test Control Center at the B test complex will provide approval to proceed into the test. One of the first actions on hot fire day will be to load the stage’s huge tanks with more than 700,000 gallons of propellant. Six barges filled with liquid hydrogen and oxygen will supply the propellant to the B-2 test stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, where the Green Run tests are taking place. The engines use cryogenic, or supercooled, liquid hydrogen as fuel and liquid oxygen as oxidizer to create combustion.
To fill each of the six barges, three for liquid oxygen and three for liquid hydrogen, it required 18 to 20 tanker trucks worth of propellant. The barges are towed by tug from a fuel depot at Stennis to the B-2 stand.
In this video, SLS Stages Manager Julie Bassler, describes avionics and flight software testing conducted in the Systems Integration Laboratory at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, to support Green Run. The computers and avionics are the “brains” of the rocket, and they control the core stage systems during the test, just like they will be required to control the rocket during the Artemis I flight.
Learn more about Green Run, and check back at this blog for updates on the SLS core stage hot fire test.

 Last week during checkouts for the second hot fire test, data indicated the valve (a type of valve called a pre-valve) was not working properly. The valve is part of the core stage’s main propulsion system and is opened at the beginning of the test and closed if necessary to stop the flow of liquid oxygen from the core stage propellant tank to the respective RS-25 engine during the hot fire.
Last week during checkouts for the second hot fire test, data indicated the valve (a type of valve called a pre-valve) was not working properly. The valve is part of the core stage’s main propulsion system and is opened at the beginning of the test and closed if necessary to stop the flow of liquid oxygen from the core stage propellant tank to the respective RS-25 engine during the hot fire.