NASA’s new Orion spacecraft received finishing touches Thursday, marking the conclusion of construction on the first spacecraft designed to send humans into deep space beyond the moon, including a journey to Mars that begins with its first test flight Dec. 4.
The assembled Orion crew module, service module, launch abort system and adapter will reside in Kennedy’s Launch Abort System Facility until its scheduled rollout to the launch pad, set for Nov. 10. At the launch pad, it will be lifted onto the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket that will carry it into space for its uncrewed flight test.
“This is just the first of what will be a long line of exploration missions beyond low earth orbit, and in a few years we will be sending our astronauts to destinations humans have never experienced,” said Bill Hill, deputy associate administrator for Exploration Systems Development “It’s thrilling to be a part of the journey now, at the beginning.”
The December flight test will send Orion 3,600 miles from Earth on a two-orbit flight intended to ensure the spacecraft’s critical systems are ready for the challenges of deep space missions.
During the 4.5-hour flight, called Exploration Flight Test-1, Orion will travel farther than any crewed spacecraft has gone in more than 40 years, before returning to Earth at speeds near 20,000 mph and generating temperatures up to 4,000 degrees Fahrenheit.


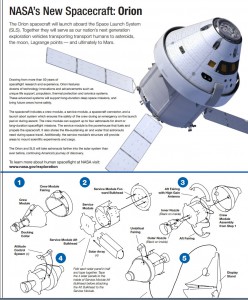 You can download and print out
You can download and print out 
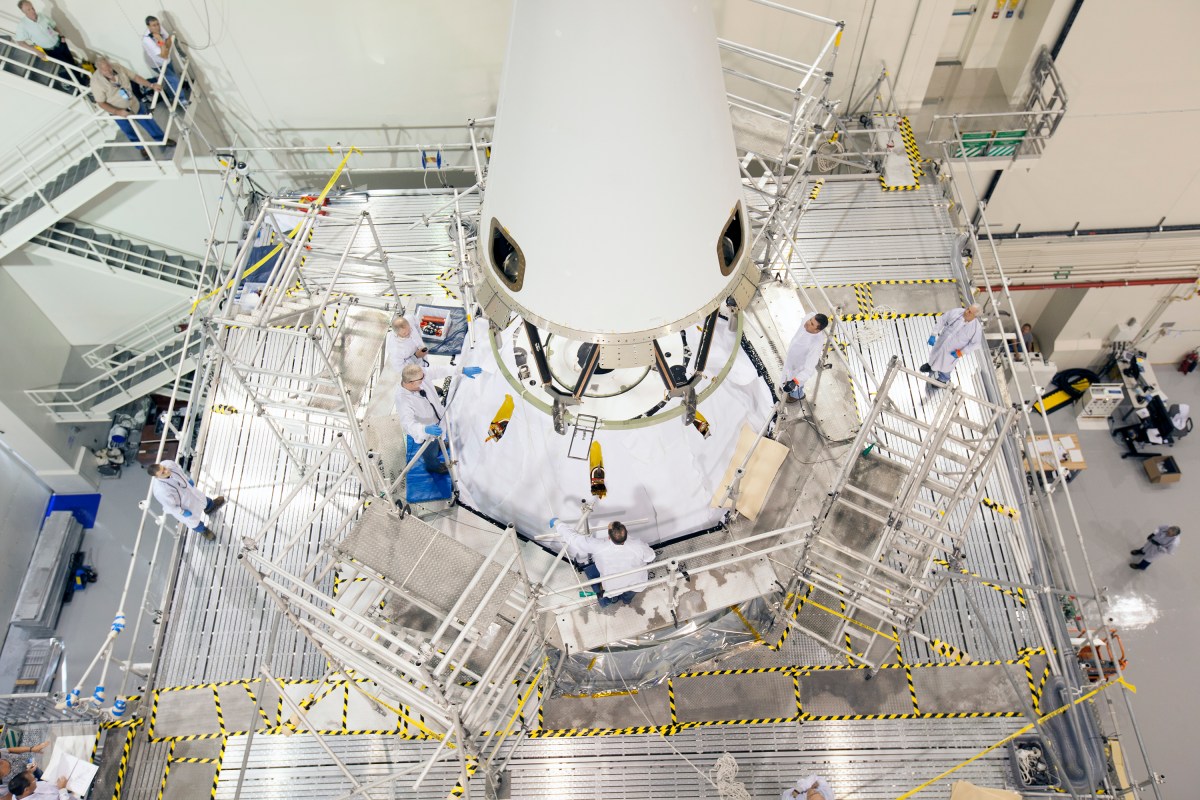




 Technicians and engineers at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida installed the Launch Abort System atop the Orion spacecraft Friday as launch preparations continue for December’s launch. The LAS, as it is known, will not be active during this flight test but would, during future flights, be equipped to act within milliseconds to pull the spacecraft and its astronaut crew away from its rocket so the Orion could parachute back to Earth safely. For the upcoming Orion flight test, the LAS will have an active jettison motor so it can pull itself and the nose fairing away from the spacecraft just before Orion goes into orbit.
Technicians and engineers at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida installed the Launch Abort System atop the Orion spacecraft Friday as launch preparations continue for December’s launch. The LAS, as it is known, will not be active during this flight test but would, during future flights, be equipped to act within milliseconds to pull the spacecraft and its astronaut crew away from its rocket so the Orion could parachute back to Earth safely. For the upcoming Orion flight test, the LAS will have an active jettison motor so it can pull itself and the nose fairing away from the spacecraft just before Orion goes into orbit.


