Sep. 03, 2020 – NASA Eyes Typhoon Haishen’s 10 Mile-wide Eye
NASA’s Terra satellite’s visible image of Typhoon Haishen revealed a small “pinhole” eye surrounded by several hundred miles of thunderstorms spiraling around it as it continued moving north though the Northwestern Pacific Ocean.
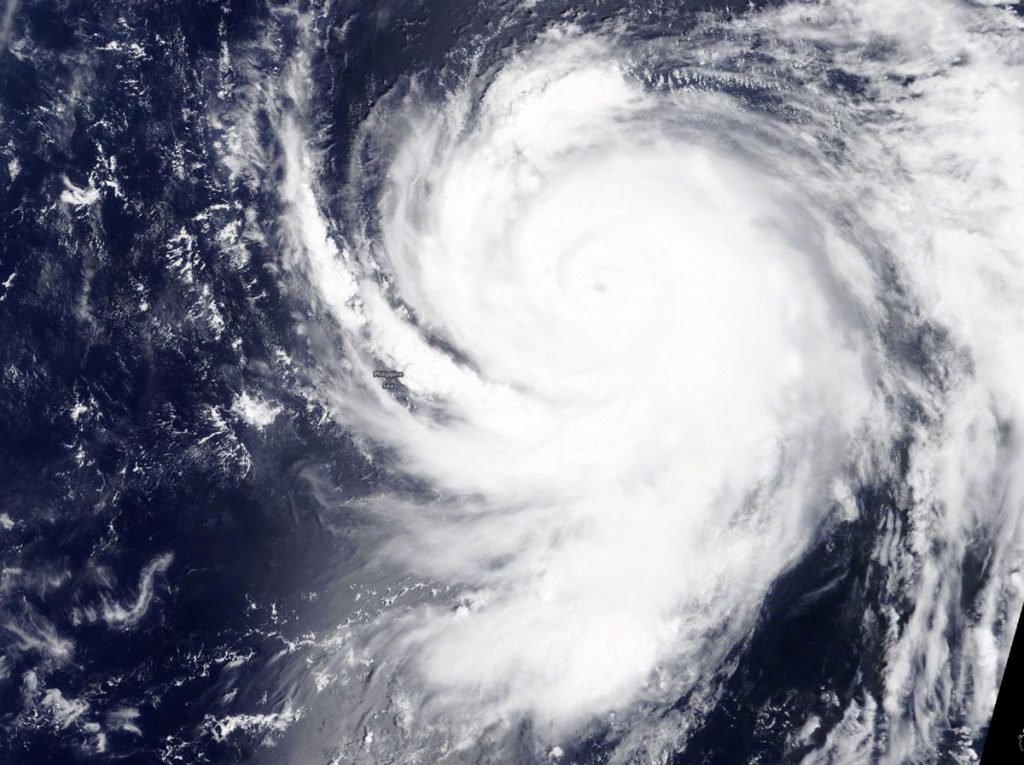
NASA Satellite View: Haishen’s Organization
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument that flies aboard NASA’s Terra satellite captured a visible image of Typhoon Haishen on Sept. 3 at 0145 UTC (Sept. 2 at 9:45 p.m. EDT). Satellite imagery shows deep convection and spiral banding of thunderstorms wrapping tightly around the 10 nautical-mile wide eye and into a low-level circulation center.
Satellite imagery was created using NASA’s Worldview product at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md.
Haishen on Sept. 1
At 5 a.m. EDT (0900 UTC) on Sept. 3, the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) in Honolulu, Hawaii noted that Typhoon Haishen was located about 646 nautical miles east-southeast of Kadena Air Base, Okinawa Island, Japan. It was centered near latitude 20.7 degrees north and longitude 137.7 degrees east. Haishen was moving to the northwest with maximum sustained winds of 95 knots (109 mph/176 kph).
Haishen is forecast to turn northwest while intensifying to 130 knots (150 mph/241 kph) within the next two days. The storm will pass west of Kyushu, Japan to make landfall in South Korea after 4 days.
About NASA’s Worldview and Terra Satellite
NASA’s Earth Observing System Data and Information System (EOSDIS) Worldview application provides the capability to interactively browse over 700 global, full-resolution satellite imagery layers and then download the underlying data. Many of the available imagery layers are updated within three hours of observation, essentially showing the entire Earth as it looks “right now.”
NASA’s Terra satellite is one in a fleet of NASA satellites that provide data for hurricane research.
Tropical cyclones/hurricanes are the most powerful weather events on Earth. NASA’s expertise in space and scientific exploration contributes to essential services provided to the American people by other federal agencies, such as hurricane weather forecasting.
For updated forecasts, visit: www.nhc.noaa.gov
