July 26, 2019 – NASA Finds Two Areas of Strength in Tropical Storm Nari
NASA’s Terra satellite found two small areas of strength in Tropical Storm Nari on July 26 as it began to affect Japan.
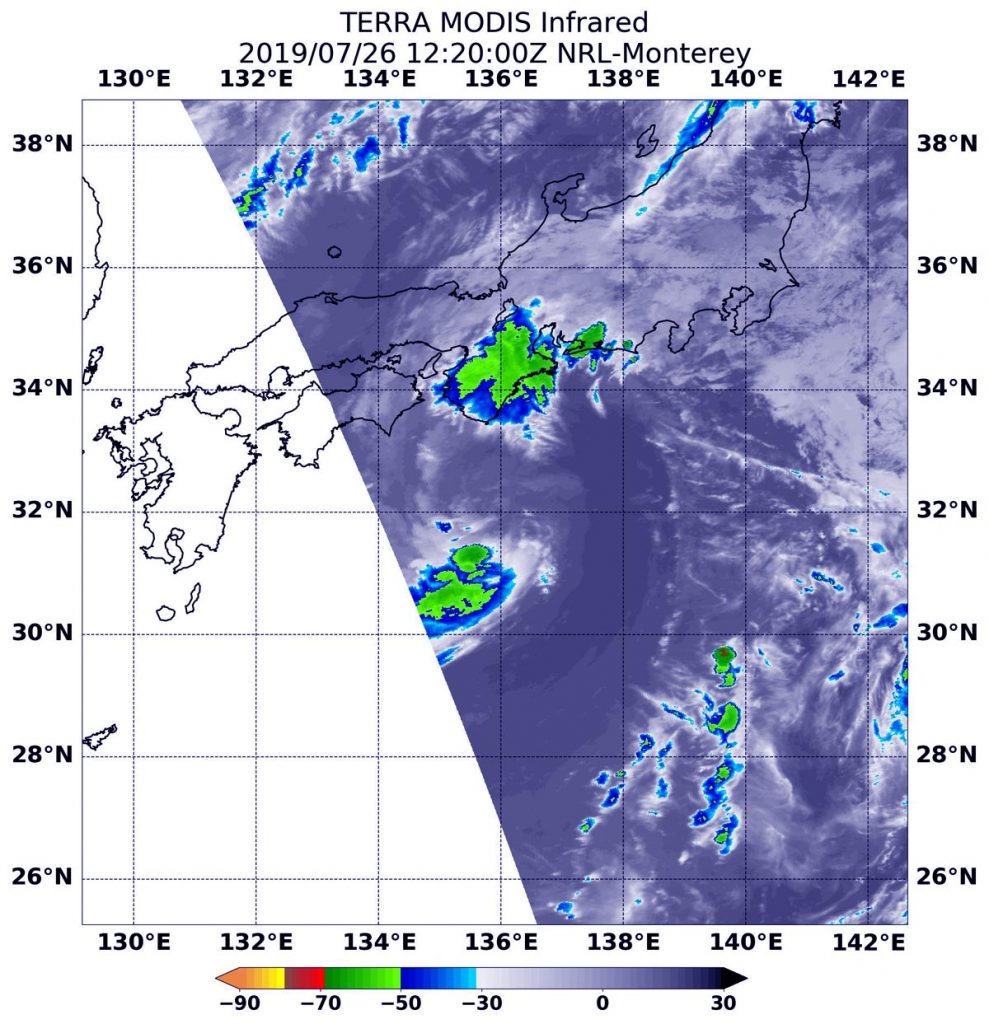
NASA’s Terra satellite uses infrared light to analyze the strength of storms by providing temperature information about the system’s clouds. The strongest thunderstorms that reach high into the atmosphere have the coldest cloud top temperatures.
On July 26 at 8:20 a.m. EDT (1220 UTC), the Moderate Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument that flies aboard NASA’s Terra satellite gathered infrared data on Nari, formerly known as Tropical Storm 07W. There were two areas of strongest storms in Tropical Storm Nari, and they were north and south of the center of circulation. In those areas, thunderstorms had cloud top temperatures as cold as minus 50 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 45.5 Celsius). That northernmost area of strong storms was located over the Kyoto, Osaka and Wakayama Prefectures of Japan.
At 5 a.m. EDT (0900 UTC), the center of Tropical Storm Nari was located near latitude 30.9 degrees north and longitude 136.3 degrees east. That’s about 314 nautical miles southwest of Yokosaka, Japan. The tropical storm is moving toward the north-northwest. Maximum sustained winds were near 40 mph (35 knots/64 kph).
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) forecast for Nari brings the storm northward, with a turn to the east in 12 hours. JTWC said “The system is expected to maintain intensity prior to Landfall in Honshu. The system is expected to dissipate by 48 hours due to passage over land and cooler water to the east of Honshu.”

