Apr. 29, 2019 – NASA Shows Winds Causing Tropical Cyclone Lorna’s Demise
NASA’s Aqua satellite saw Tropical Cyclone Lorna was being torn apart by strong northwesterly wind shear in the Southern Indian Ocean.
In general, wind shear is a measure of how the speed and direction of winds change with altitude. Tropical cyclones are like rotating cylinders of winds. Each level needs to be stacked on top each other vertically in order for the storm to maintain strength or intensify. Wind shear occurs when winds at different levels of the atmosphere push against the rotating cylinder of winds, weakening the rotation by pushing it apart at different levels.
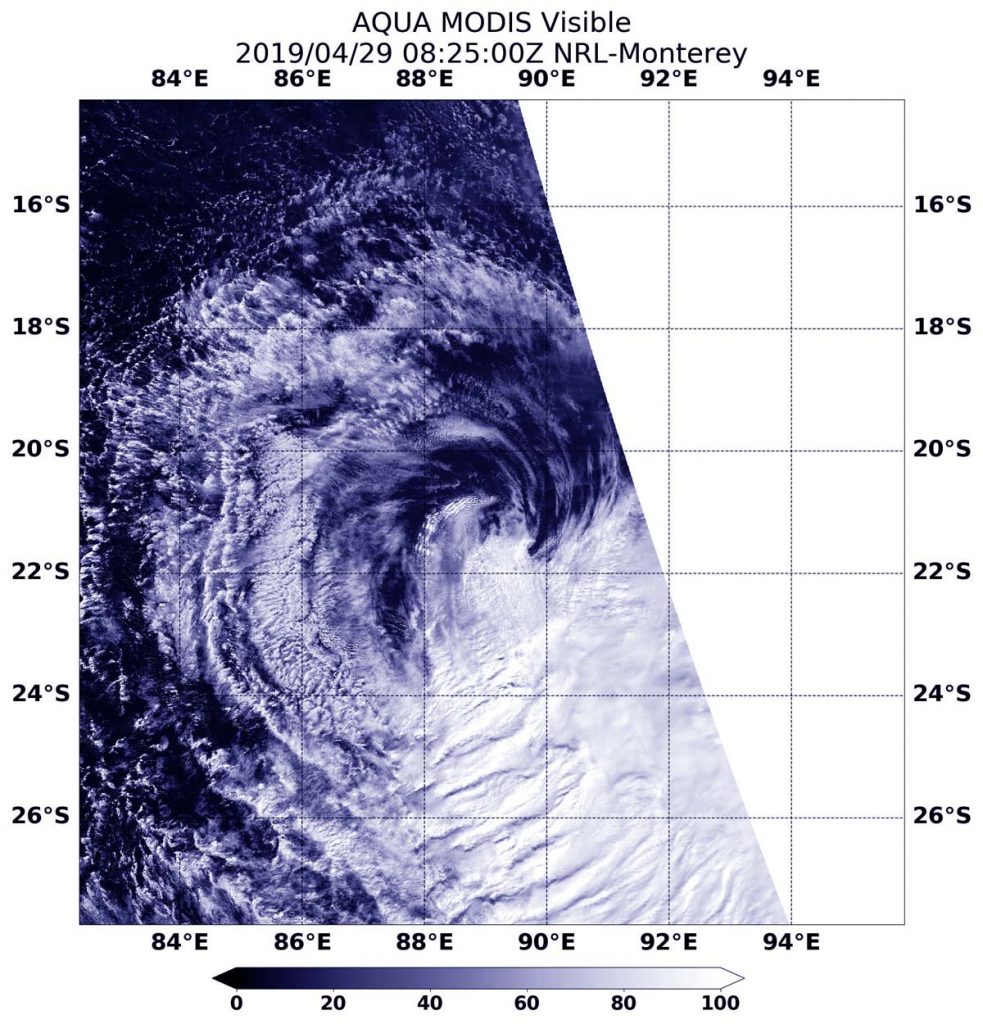
On April 29 at 4:29 a.m. EDT (0829 UTC), the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument aboard NASA’s Aqua satellite provided a visible image of Lorna. Northwesterly winds were pushing the bulk of Lorna’s clouds far southeast of its center.
At 11 a.m. EDT (1500 UTC), the Joint Typhoon Warning Center or JTWC issued their final warning in Lorna. At that time, JTWC noted that Tropical Cyclone Lorna was located near 22.1 degrees south latitude and 88.8 degrees east longitude. That is 738 nautical miles southwest of Cocos Island. Lorna was moving to the south-southwest. Maximum sustained winds dropped to 35 knots (40 mph/65 kph) and the storm was getting weaker.
Lorna is rapidly weakening under adverse atmospheric conditions. The JTWC noted that the “environment is very hostile with extremely high (50 to 60 knot/57 to 69 mph/ /92 to 111 kph) vertical wind shear,” which is tearing the storm apart. Lorna is forecast to dissipate by April 30.
