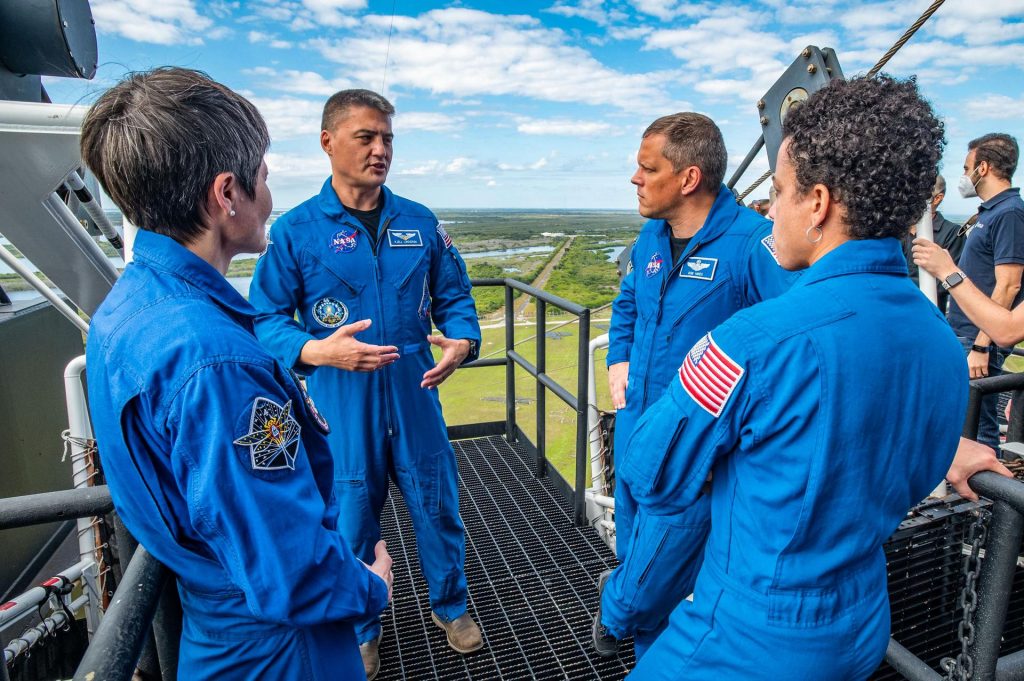
NASA and SpaceX managers have gathered at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to start the Crew-4 mission’s Flight Readiness Review (FRR). Over the next several hours, the FRR will focus on the preparedness of SpaceX’s crew transportation system, the International Space Station, and its international partners to support the flight, and the certification of flight readiness.
After the conclusion of the FRR, NASA will hold a media teleconference to discuss the outcome. While the teleconference will not be televised, media may call in to ask questions via phone. Contact the Kennedy newsroom no later than 4 p.m. EDT for connection details.
Participants in the teleconference include:
- Kathy Lueders, associate administrator, Space Operations Mission Directorate, NASA Headquarters
- Steve Stich, manager, Commercial Crew Program, Kennedy
- Joel Montalbano, manager, International Space Station, NASA’s Johnson Space Center
- Zeb Scoville, chief flight director, Flight Operations Directorate, Johnson
- Frank De Winne, program manager, International Space Station, ESA
NASA astronauts Kjell Lindgren, Robert Hines, and Jessica Watkins, and ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Samantha Cristoforetti will launch on SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft for the Crew-4 mission as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. They will arrive at the International Space Station approximately 24 hours after launch. Crew-4 will arrive at station for a short overlap with NASA astronauts Raja Chari, Tom Marshburn, and Kayla Barron, and ESA astronaut Matthias Maurer, who flew to the station as part of the agency’s SpaceX Crew-3 mission in November 2021.