by Lance D. Davis
Did you know our planet has two types of seasons? They are meteorological and astronomical. What’s the difference?
“Meteorological seasons” follow the changing of the calendar, month to month, and are based on the annual temperature cycle – seasonal temperature variations modified by fluctuations in the amount of solar radiation received by Earth’s surface over the course of a year. For instance, the meteorological season of spring begins each year on March 1 and will end on May 31.
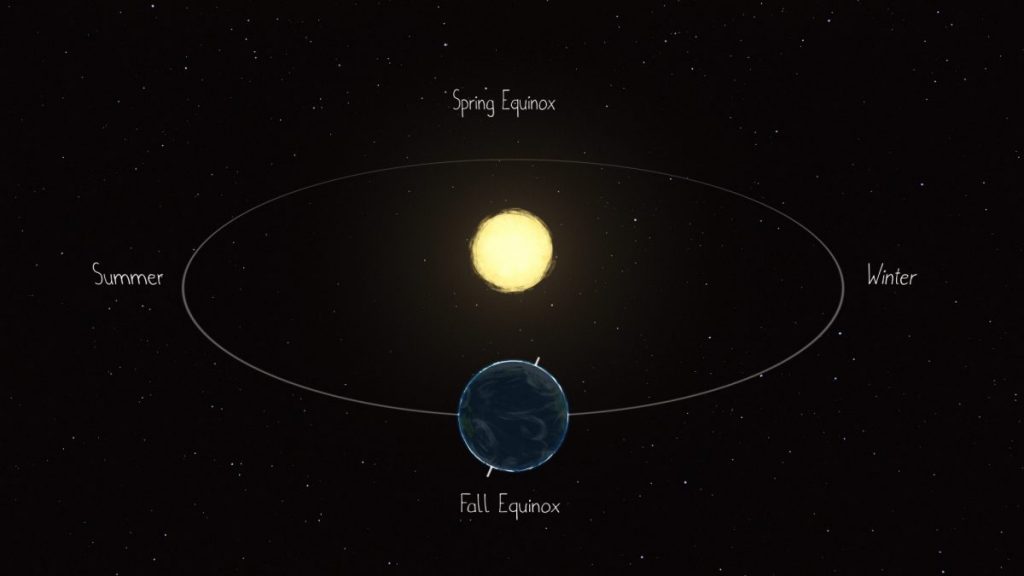
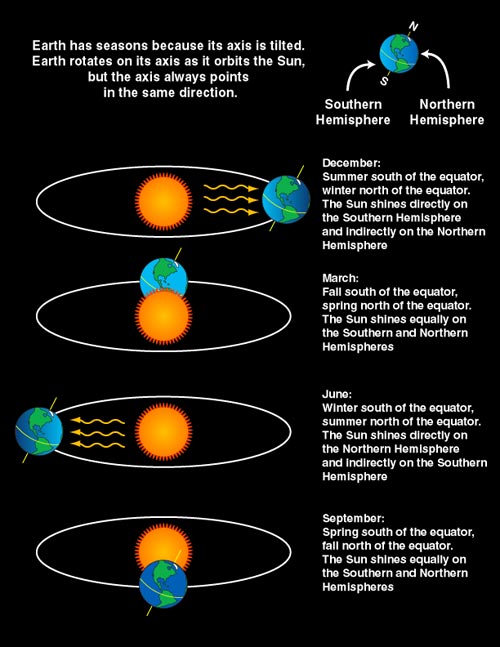
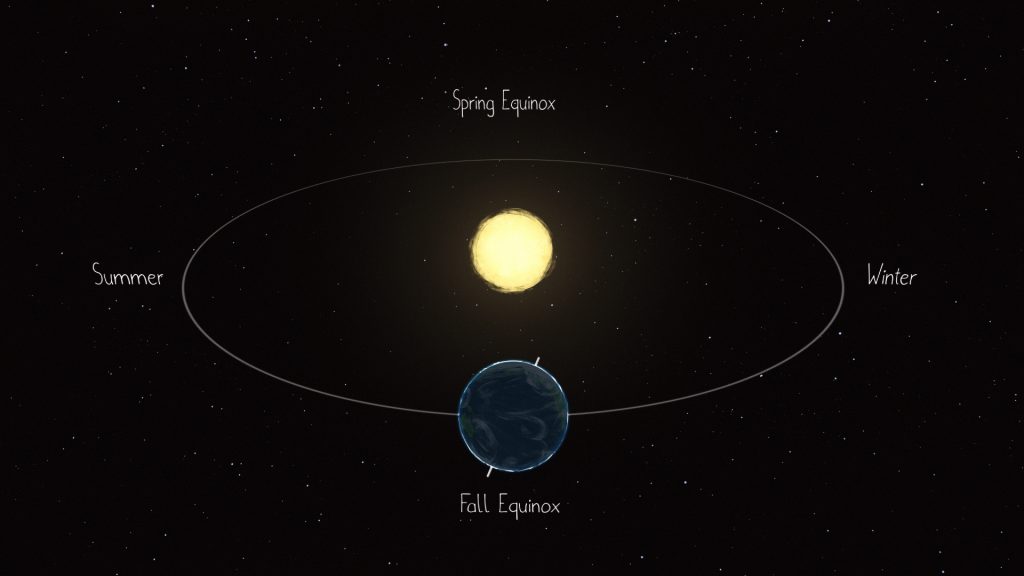
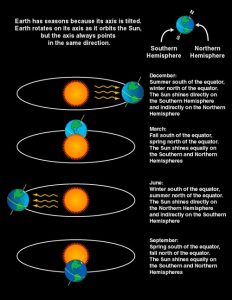
However, “astronomical” seasons happen because of the tilt of Earth’s axis (with respect to the Sun-Earth plane), and our planet’s position during its orbit around the Sun.
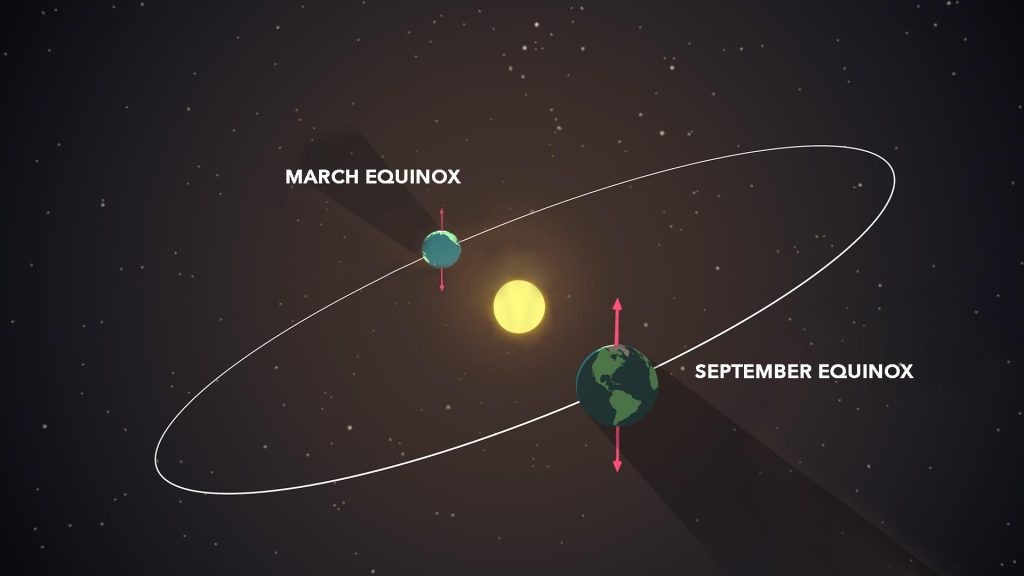
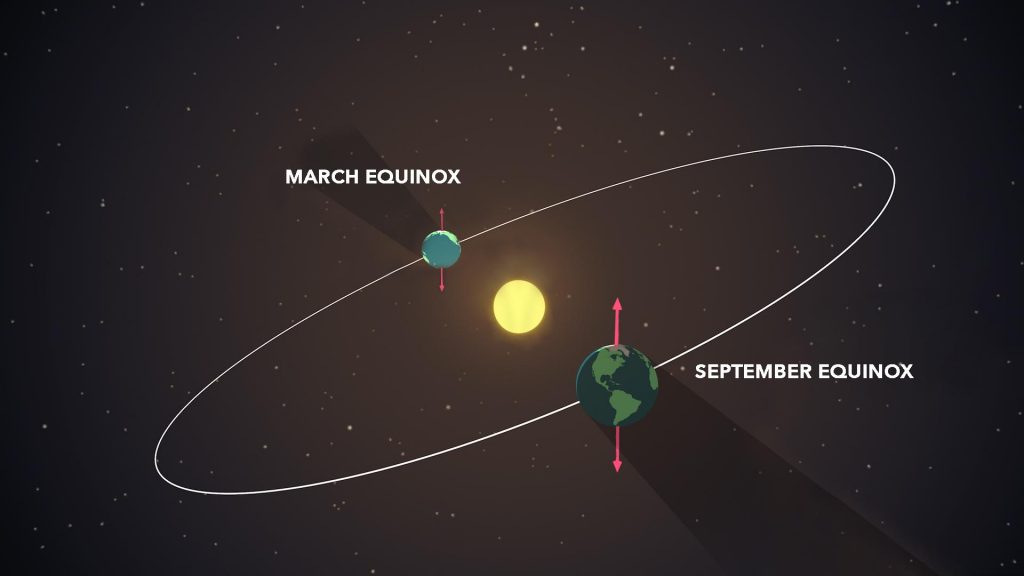
The March equinox – also called the vernal equinox – is the astronomical beginning of the spring season in the Northern Hemisphere. Seasons are reversed in the Southern Hemisphere where it will be autumn, also known as fall. These simultaneous seasons will occur March 20, 2022, at 15:33 UTC (Coordinated Universal Time) or 10:33 a.m. CDT (Central Daylight Time).
The Sun will pass directly above the equator, bringing nearly equal amounts of day and night on all parts of Earth. At the equator, an equinox results in about 12 hours of daylight and 12 hours of night.
Equinoxes and solstices are caused by Earth’s tilt on its axis and the ceaseless motion it has while orbiting the Sun. Think of them like events happening as our planet make its journey around the Sun.
North of the equator, the March equinox will also bring us earlier sunrises, later sunsets, softer winds, and budding plants. With the reversed season, those south of the equator will experience later sunrises, earlier sunsets, chillier winds, and dry, falling leaves.
If you’re in the Northern Hemisphere, watch the Sun as it sets just a bit farther north on the horizon each evening until the June solstice – when the Sun reverses directions, moving back to the south. Also, get outside to enjoy the warmer weather and extended daylight!
Happy March equinox, Earthlings!