Well over 100 people in California, Nevada, Arizona and Oregon observed a fireball at 5:35 p.m. PST Dec. 19. This event was unusual not for the brightness of the fireball—similar to that of a crescent Moon—but for the persistent train left behind after the object ablated. This persistent train lasted for minutes (compared to the one second duration of the fireball) and was caused by sunlight reflecting off dust particles left behind by the meteoroid as it broke apart in Earth’s atmosphere. Upper atmosphere winds distorted the train over time, giving it a curvy, “corkscrew” appearance.
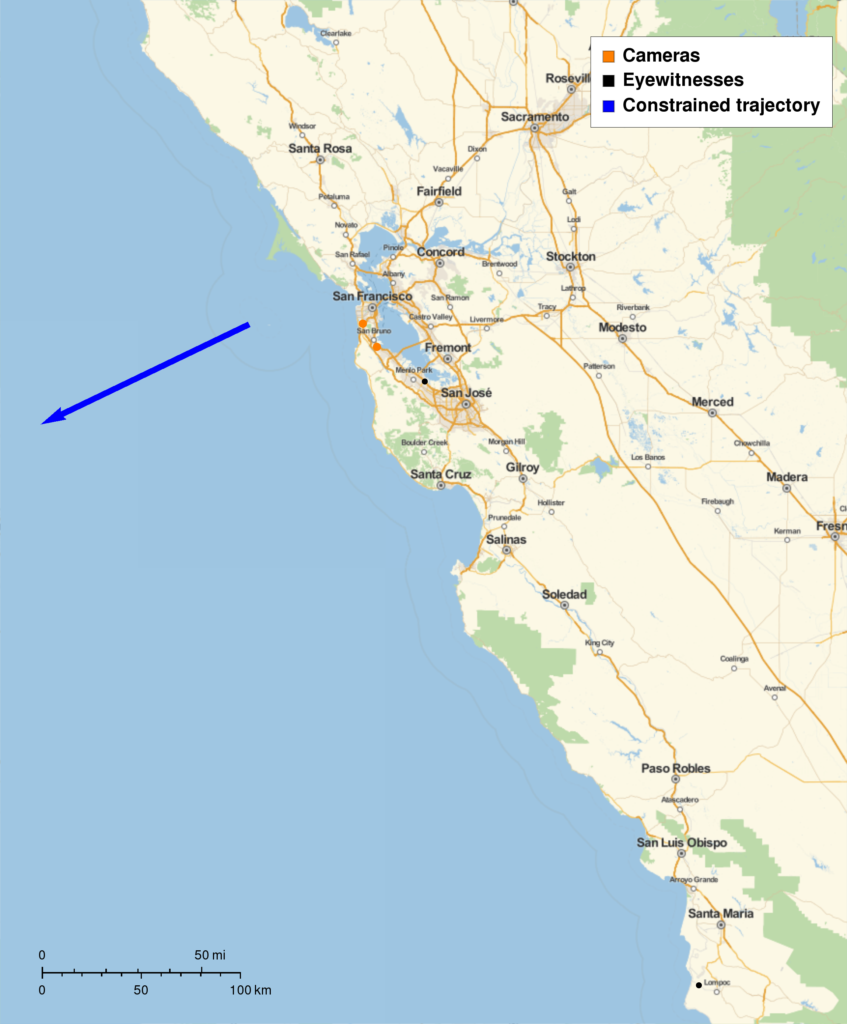
An analysis of the eyewitness accounts indicates that the meteor first became visible at an altitude of 48 miles over the Pacific Ocean some 50 miles west of the entrance to San Francisco Bay. Moving west of south at 63,000 miles per hour, it managed to survive only a second or so before ablating and breaking apart at an altitude of 34 miles above the ocean.
For videos and images of this event and the persistent train, visit the American Meteor Society website.
