As the date of the possible new May Camelopardalid meteor shower looms, we wanted to offer some answers to frequently asked questions. We hope this question and answer post will be helpful as you observe the shower.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How do you pronounce the name of this meteor shower?
A: Ask a different person and you’ll get a different answer! Common pronunciations are camel-oh-PAR-dahl-idz, kah-MEL-oh-PAR-dal-idz, and camel-oh-par-DAL-idz. It it’s too much of a tongue twister, you are camelopardon-ed. 🙂
Q: Why does this shower have such a funny name?
A: Meteor showers are named after the location of their radiant – or the point in the sky from which the meteors appear to originate. This shower is expected to produce meteors in May with a radiant in the constellation Camelopardalis.
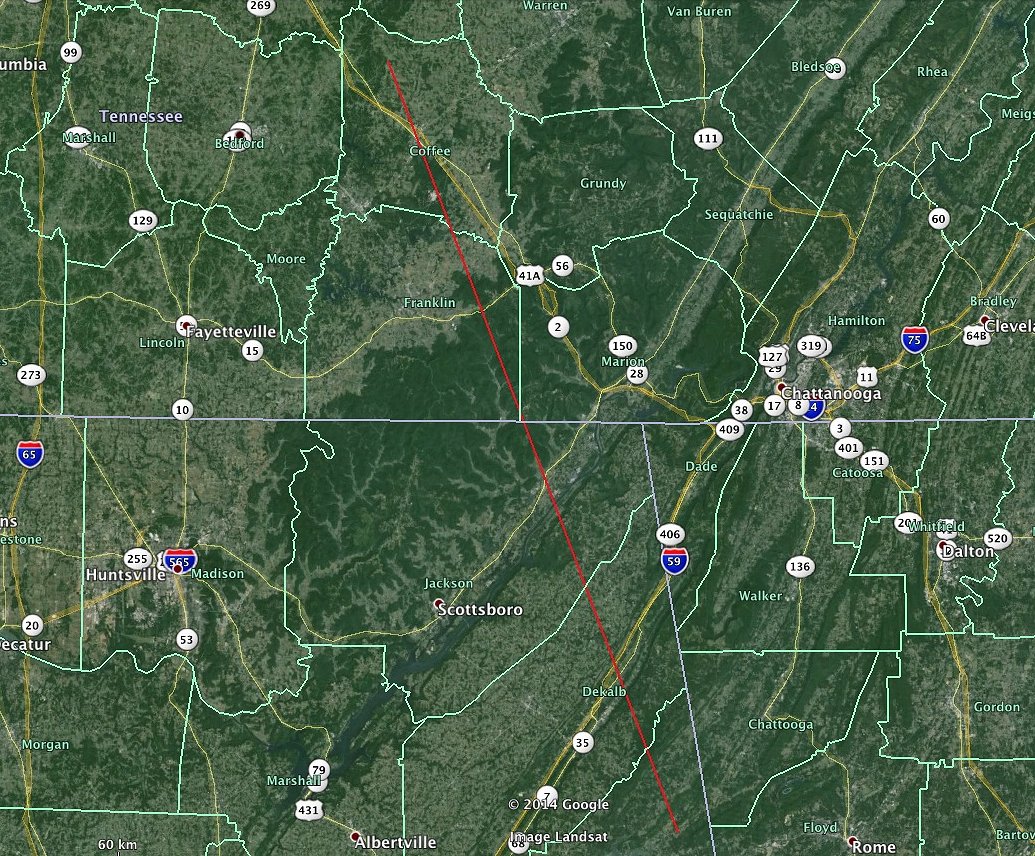
Q: Can I see the May Camelopardalids from my location in _____?
A: Check out the visibility map below. If your location is in the yellow zone, and you have clear dark skies, you should be able to see May Camelopardalids during the expected peak, if it occurs.
Q: When can I see May Camelopardalids?
A: The expected peak is between 1 and 3 am CDT on May 24.
Q: Where is the May Camelopardalid radiant?
A: The radiant is in the constellation Camelopardalis. It’s not a well-known constellation, but you can find the general direction if you look between Ursa Major and Cassiopeia.
Q: Should I look at the radiant to see May Camelopardalids?
A: Nope!
Q: Ok, where should I look then, smarty-pants?
A: If it’s not cloudy, get as far away from bright lights as you can, lie on your back, and look up. You should be able to see May Camelopardalids over the whole sky.
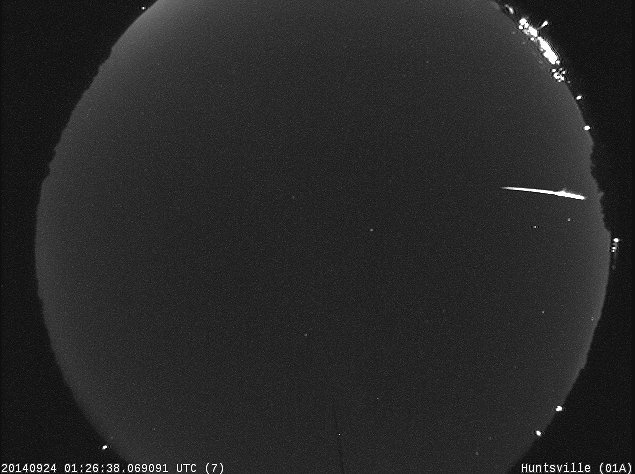
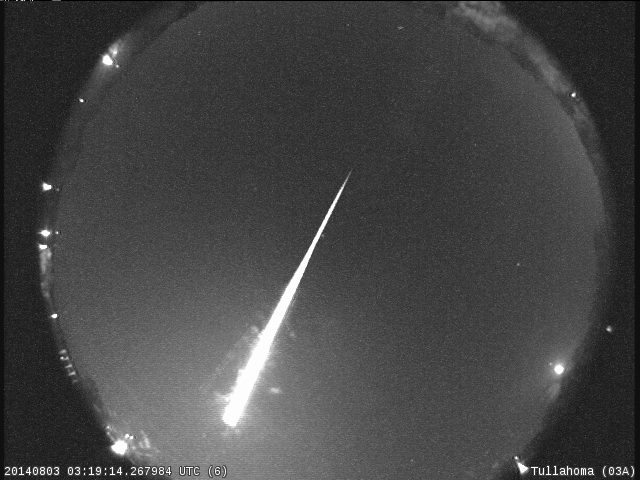
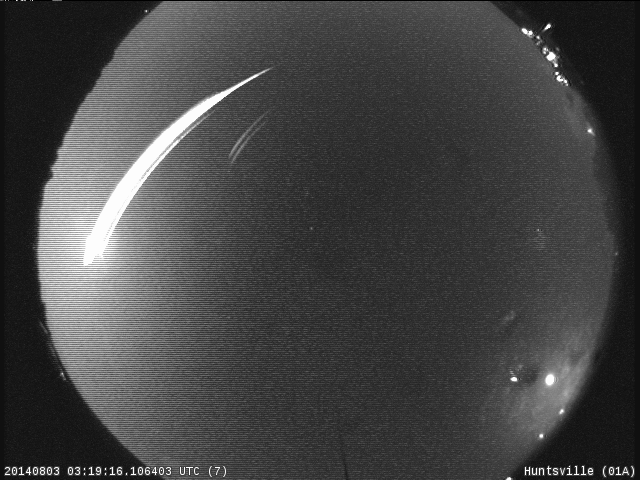
Q: How do I know if the meteor I just saw is a May Camelopardalid?
A: If you see a meteor, try to trace it’s path backwards. If you end up in the constellation Camelopardalis, there’s a good chance you’ve seen a May Camelopardalid!
Q: My skies are dark and cloud-free but I’m still not seeing any meteors! Why not?!
A: There are a couple of possibilities. (1) The comet wasn’t very active 200+ years ago, and therefore didn’t produce many meteoroids. So the meteor shower is much weaker than predicted. (2) You need to have patience. You also need to make sure your eyes are adapted to the dark – this takes about 45 minutes. Make sure you don’t keep looking at your phone or other sources of light, else your eyes will have to start the dark adaptation process all over again.
Q: Has a satellite ever been hit by a meteoroid?
A: Yes. Here are a few examples: Mariner IV, a NASA planetary exploration spacecraft encountered a meteoroid stream between the orbits of Earth and Mars in Sept 1967. The encounter damaged the thermal shield. Olympus, an ESA communication satellite, was struck by a Perseid near the time of the shower peak in August 1993. It was sent tumbling and exhausted its fuel supply.
Q: How big are May Camelopardalid meteoroids?
A: These meteoroids are expected to be anywhere from dust-grain sized to millimeter sized.
Q: How can a small bit of rock damage a satellite?
A: Meteoroids travel very fast and therefore have a lot of energy. The May Camelopardalids will be traveling slowly, as far as meteors go, but they will still be moving at 36,000 mph! That’s about 27 times faster than the Concorde jet!
You can get more facts about the May Camelopardalids here.
How do you say Camelopardalids? Find out here!
Watch our live feed of the shower: http://www.ustream.tv/channel/nasa-msfc