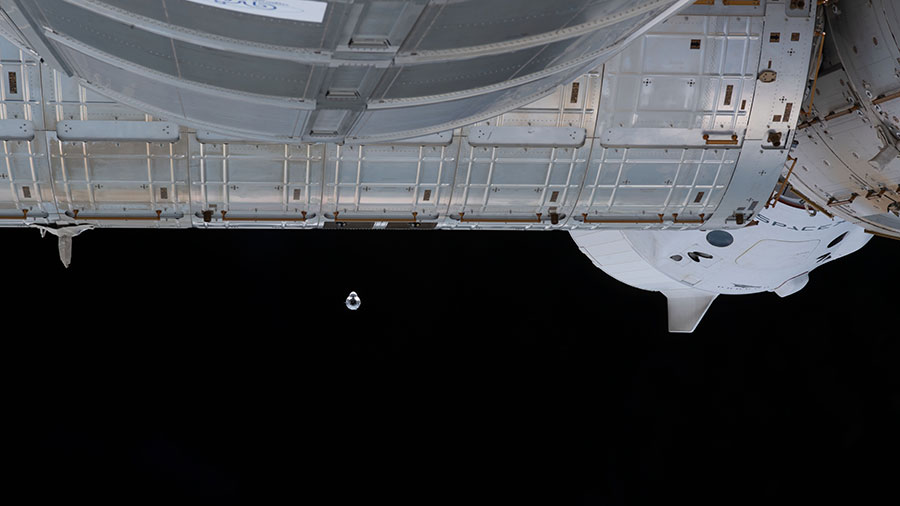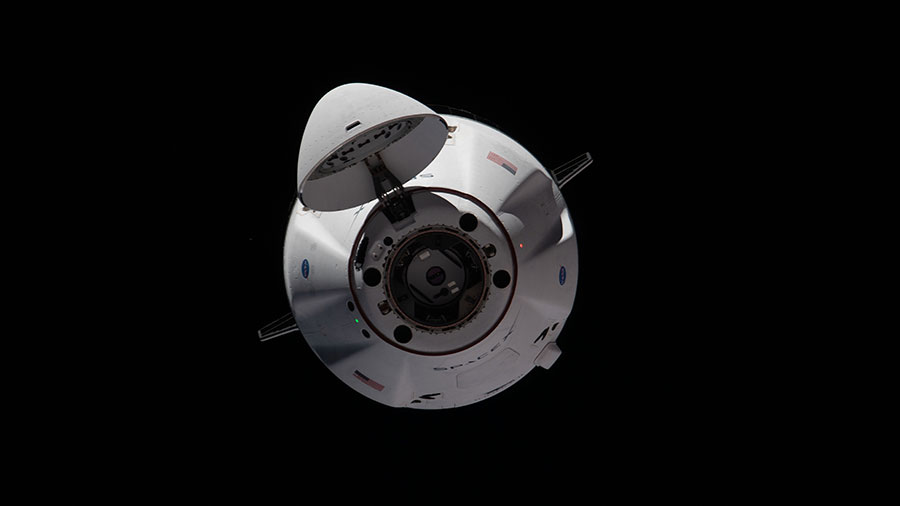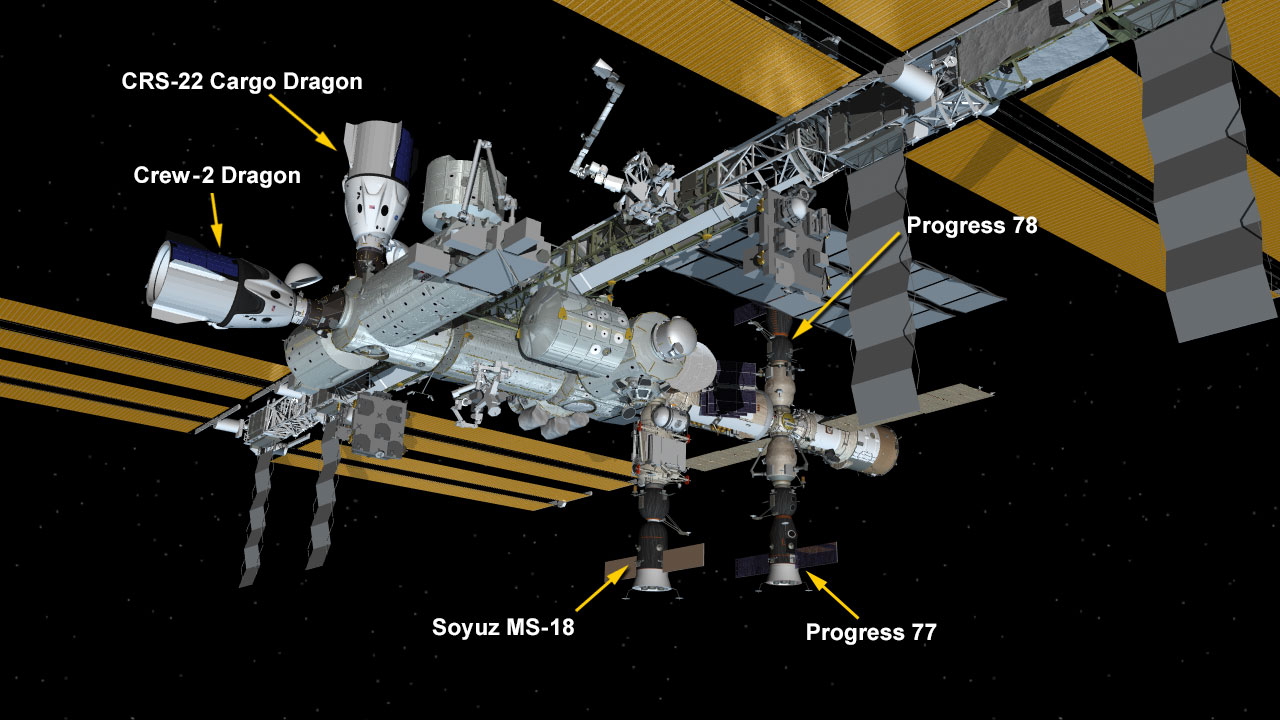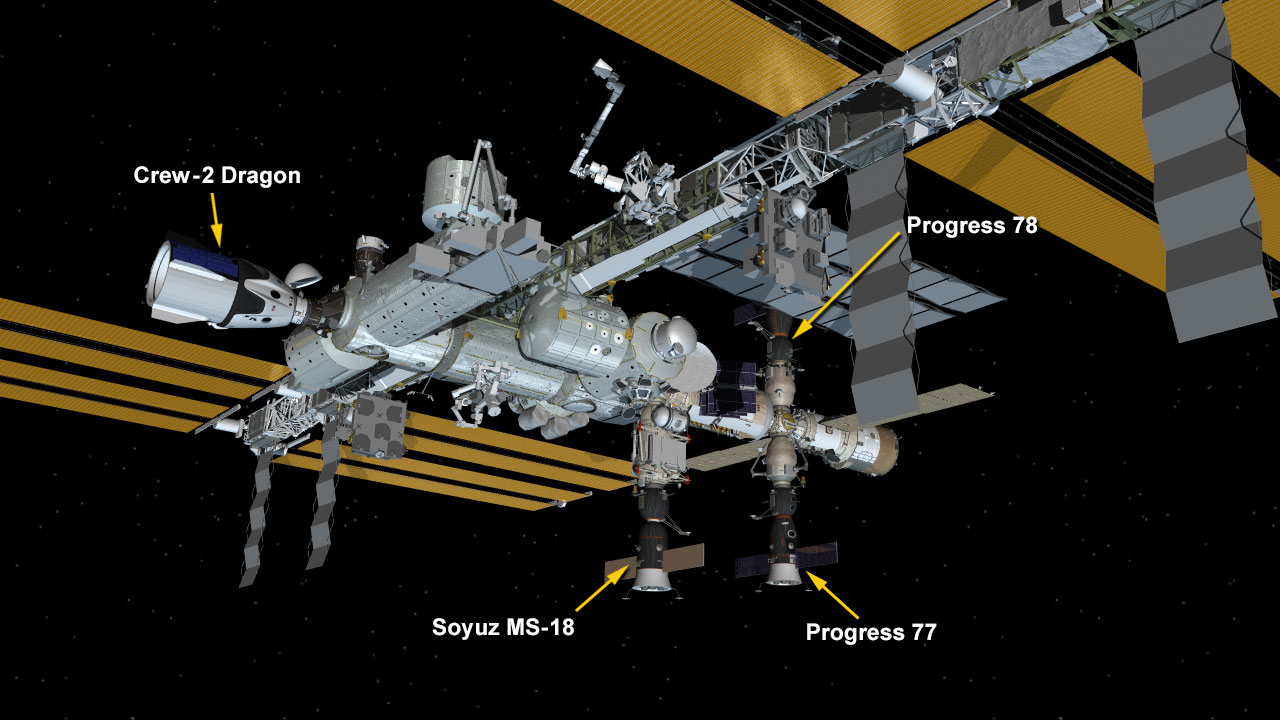
With NASA astronaut Shane Kimbrough monitoring aboard the International Space Station, a SpaceX cargo Dragon spacecraft undocked from the International Docking Adapter on the station’s space-facing port of the Harmony module at 10:45 a.m. EDT.
Dragon will fire its thrusters to move a safe distance from the space station during the next 36 hours. On Friday, July 9, Dragon will conduct a deorbit burn to begin its re-entry sequence into Earth’s atmosphere. Dragon is expected to splash down at approximately 11:29 p.m. in the Gulf of Mexico near Tallahassee, Florida. The splashdown will not be broadcast.
Splashing down off the coast of Florida enables quick transportation of the science aboard the capsule to the agency’s Kennedy Space Center’s Space Station Processing Facility, delivering some science back into the hands of the researchers as soon as four to nine hours after splashdown. This shorter transportation timeframe allows researchers to collect data with minimal loss of microgravity effects. The Dragon’s departure will be the second splashdown of a U.S. commercial cargo craft off the Florida coast. Previous cargo Dragon spacecraft returned to the Pacific Ocean, with quick-return science cargo processed at SpaceX’s facility in McGregor, Texas, and delivered to NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston.
Dragon launched June 3 on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy, arriving at the station a little less than 16 hours later. The spacecraft delivered more than 7,300 pounds of research investigations, crew supplies, and vehicle hardware to the orbiting outpost. Dragon’s external cargo “trunk” carried six new ISS Roll-Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs), two of which Expedition 65 crew members Kimbrough and Thomas Pesquet, an ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut, installed during three spacewalks June 16, 20, and 25.
Some of the scientific investigations Dragon will return to Earth include:
- Lyophilization-2 examines how gravity affects freeze-dried materials and could result in improved freeze-drying processes for pharmaceutical and other industries. Freeze-drying also has potential use for long-term storage of medications and other resources on future exploration missions.
- Molecular Muscle Experiment-2 tests a series of drugs to see whether they can improve health in space, possibly leading to new therapeutic targets for examination on Earth.
- Oral Biofilms in Space studies how gravity affects the structure, composition, and activity of oral bacteria in the presence of common oral care agents. Findings could support development of novel treatments to fight oral diseases such as cavities, gingivitis, and periodontitis.
Learn more about station activities by following the space station blog, @Space_Station and @ISS_Research on Twitter as well as the ISS Instagram and ISS Facebook accounts.