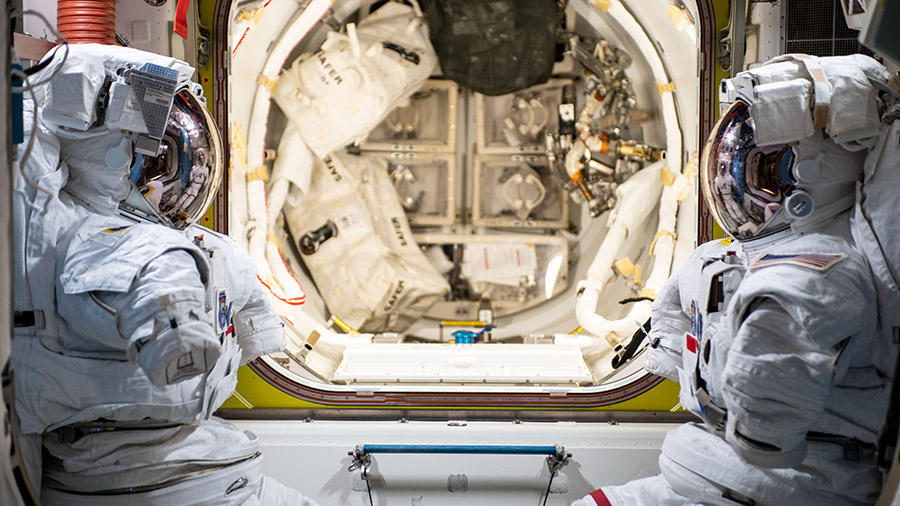
Two astronauts are checking out their gear today ahead of a spacewalk planned for the end of the month. The duo along with the rest of the Expedition 66 crew also had time set aside for human research, robotics, and physics aboard the International Space Station.
NASA Flight Engineers Thomas Marshburn and Kayla Barron are getting ready for a six-and-a-half hour spacewalk scheduled for Nov. 30. The duo will exit the U.S. Quest airlock, translate over to the Port-1 truss segment, and replace a faulty antenna system. Today, the astronauts checked out spacewalking gear and inspected the tethers that will keep them attached to the station.
Afterward, Barron partnered again with NASA Flight Engineer Raja Chari for the GRASP experiment studying how microgravity affects hand-eye coordination and the vestibular system. The pair took turns wearing a virtual reality headset reaching for virtual objects to understand how the central nervous system adapts to weightlessness.
Marshburn worked throughout Tuesday collecting and stowing his blood samples in a science freezer for later analysis. The three-time station visitor also contributed to the Food Physiology study that explores the effects of diet on astronauts living long-term in space.
Flight Engineer Matthias Maurer of ESA (European Space Agency) studied advanced robotic maneuvers today using the Astrobee robotic free-flyers. NASA astronaut Mark Vande Hei set up the Microgravity Science Glovebox to learn how to harness nanoparticles to fabricate and manufacture new materials for the InSPACE-4 physics study.
Cosmonauts Anton Shkaplerov and Pyotr Dubrov had a physical fitness test today on the station’s exercise bicycle. The Roscosmos duo strapped sensors to themselves and measured their cardiovascular function during this morning’s test. The pair split up in the afternoon and worked on life support maintenance and cargo inventory tasks.