Astra has completed final liquid oxygen conditioning and resumed countdown for the launch of its Rocket 3, carrying two of NASA’s TROPICS CubeSats. Liftoff currently is scheduled for today at 1:43 p.m. EDT.
Astra has completed final liquid oxygen conditioning and resumed countdown for the launch of its Rocket 3, carrying two of NASA’s TROPICS CubeSats. Liftoff currently is scheduled for today at 1:43 p.m. EDT.
Astra has paused the countdown of the launch of its Rocket 3, carrying two of NASA’s TROPICS CubeSats, to complete final liquid oxygen conditioning on the vehicle. Upon completion, the team will set a new launch time for TROPICS-1.

Each TROPICS satellite is identical – a 3U CubeSat about the size of a loaf of bread and weighing about 12 lbs.
The TROPICS CubeSat payload is a spinning microwave radiometer with highly integrated, compact microwave receiver electronics.
TROPICS satellite measures microwave frequencies ranging from about 90 to 205 gigahertz, which can monitor the atmospheric emissions made by water vapor, oxygen, and clouds in the atmosphere.
TROPICS target altitude is 550 kilometers, and pairs of CubeSats will have three slightly different low-Earth orbits, all at an angle about 30 degrees above the equator.
The TROPICS Pathfinder satellite, a proof-of-concept CubeSat that launched in June of 2021, has captured images of several tropical cyclones, such as Hurricane Ida over the United States, Cyclone Batsirai over Madagascar, and Super Typhoon Mindulle over eastern Japan. The pathfinder satellite has also provided the TROPICS research team an opportunity to fine tune the satellites’ software and operational procedures before the constellation launches. In addition, the pathfinder has already been calibrated and will be able to serve as a calibration reference for the rest of the TROPICS constellation satellites. The TROPICS pathfinder helps the TROPICS CubeSats start producing useful data quickly.
Astra’s Rocket 3 is an expendable, vertically-launched two stage rocket that uses liquid oxygen and kerosene as propellants. It has an overall length of 43 feet and is 52 inches in diameter. Astra designed it to fit inside a standard shipping container. Rocket 3 has five engines on its first stage, and one engine on its second stage.
TROPICS is an Earth venture instrument mission – science-driven, competitively selected, low-cost missions that provide opportunity for investment in innovative Earth science to enhance our capability to better understand the current state of the Earth system and to enable continual improvement in the prediction of future changes.
The TROPICS team is led by Principal Investigator Dr. William Blackwell at Massachusetts Institute of Technology’s (MIT) Lincoln Laboratory in Lexington and includes researchers from NASA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), and several universities and commercial partners.
NASA’s Launch Services Program at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida manages the launch service.

NASA’s TROPICS CubeSats mission is scheduled to launch today, June 12, on an Astra Rocket 3 from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. A two-hour window opens at noon EDT.
Here’s a look at some of today’s upcoming milestones. All times are approximate:
COUNTDOWN
Min/Sec Event
+0s Lift-off
+6s Begin Pitch Over
+1min 10s Max-Q
+3min 00s Main Engine Cutoff (MECO)
+3min 05s Fairing separation
+3min 10s Stage separation
+3min 15s Upper stage ignition
+8min 30s Second Engine Cutoff (SECO)
+8min 40s Payload Deployment

Weather officials with Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s 45th Weather Squadron predict a 40% chance of favorable weather conditions at noon, the start of today’s launch window, with the forecast dropping to 10 percent favorable later in the afternoon.
The primary weather concern at the start of the launch window is a Cumulus Cloud Rule violation. Later in the launch window, concerns include Surface Electric Fields and Lightning rules.
TROPICS mission aims to improve observations of tropical cyclones. Six TROPICS satellites will work in concert to provide microwave observations of a storm’s precipitation, temperature, and humidity as often as every 50 minutes.
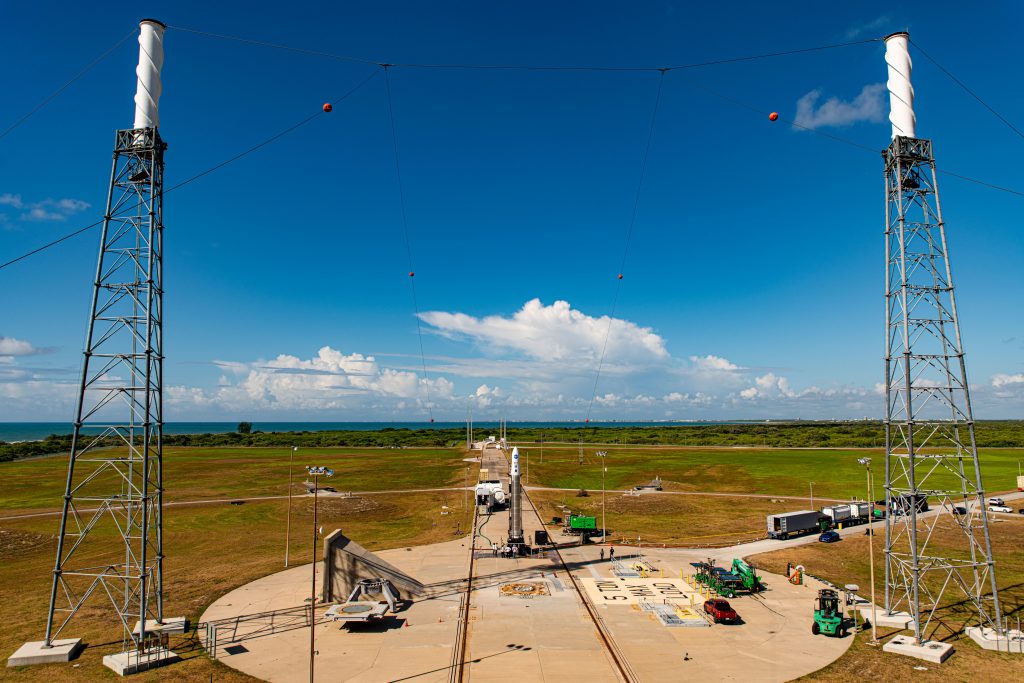

Launch day has arrived for NASA’s commercial partner Astra. A pair of small satellites wait atop Astra’s Rocket 3 for liftoff from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. This mission will send two-shoebox sized CubeSats to low-Earth orbit. A two-hour launch window opens at noon EDT.
This is the first of three planned launches for NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) mission. Together the three launches will attempt to place six satellites in three different orbital planes to study the formation and development of tropical cyclones, making observations more often than what is possible with current weather satellites. The six TROPICS satellites will join the TROPICS Pathfinder satellite, which is already in orbit.
The six TROPICS satellites will maximize their time over the part of the Earth where tropical cyclones form and will work in concert to improve observations of tropical cyclones. The spread of the satellites means that a satellite should pass over any spot in an area stretching from the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States to the southern coast of Australia about once an hour. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and cloud ice by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification. This new data, coupled with information collected from other weather satellites, will increase understanding of tropical cyclones and improve forecasting models.
Follow launch updates on this blog and stay connected with the mission on social media.
Twitter: @NASA_LSP, @NASAEarth, @NASAKennedy, @NASA, @Astra
Facebook: NASA
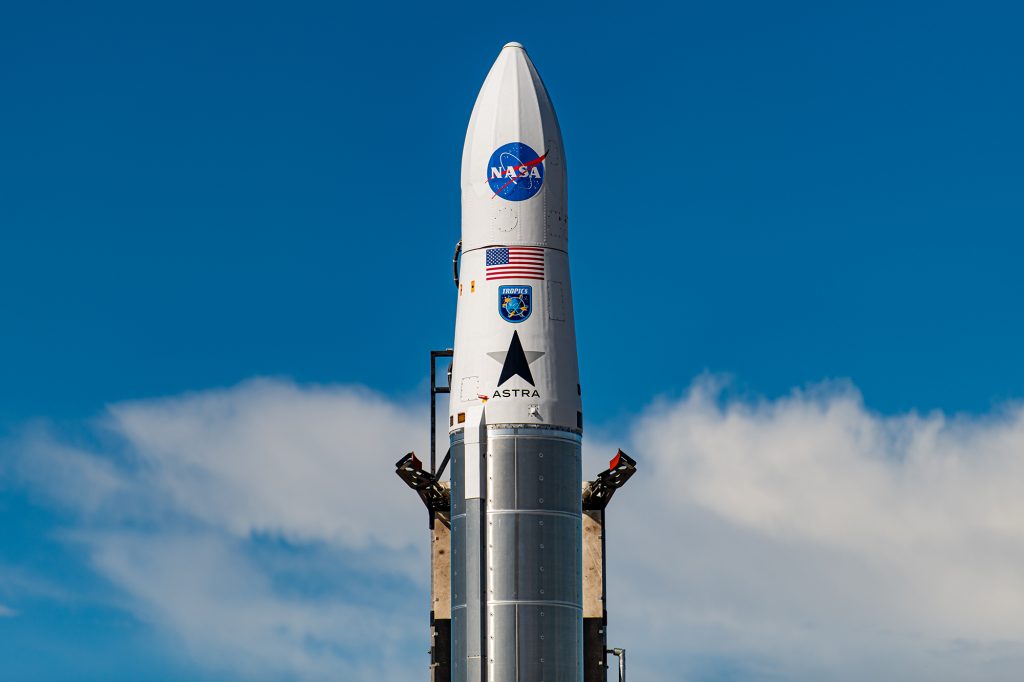
Astra Space Inc. is targeting no earlier than June 12, pending issuance of a launch license from the Federal Aviation Administration, for the first launch of NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS), a constellation of six CubeSats. Two CubeSats, each about the size of a loaf of bread, will launch aboard Astra’s Rocket 3.3 from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.
TROPICS will study tropical cyclones like hurricanes, some of the most powerful and destructive weather events on Earth, by measuring storm characteristics with a sensor about the size of a coffee cup. The miniaturized microwave radiometer detects the thermal radiation naturally emitted by the oxygen and water vapor in the air. TROPICS has the potential to provide near-hourly observations of a storm’s precipitation, temperature, and humidity. This data can help scientists increase understanding of the processes driving rapid changes in storm structure and intensity, which will improve weather forecasting models.
Astra will launch the other four TROPICS CubeSats in two separate launches later this summer.
The TROPICS team is led by Principal Investigator Dr. William Blackwell at Massachusetts Institute of Technology’s (MIT) Lincoln Laboratory in Lexington and includes researchers from NASA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), and several universities and commercial partners. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, will manage the launch service.
Stay connected with the mission on social media, and let people know you’re following it on Twitter, Facebook, and Instagram by tagging these accounts:
Twitter: @NASA, @NASAEarth, @NASA_LSP, @Astra
Facebook: NASA, NASA Earth, NASA LSP
Instagram: @NASA, @AstraSpace
NASA intends to issue a sole source modification to SpaceX to acquire five additional crewed flights to the International Space Station as part of its Commercial Crew Transportation Capabilities (CCtCap) contract. The additional crew flights will allow NASA to maintain an uninterrupted U.S. capability for human access to the space station with two unique commercial crew industry partners.
In December 2021, NASA announced the extension of the International Space Station to 2030. With this extension, there is a need for additional crew rotation missions to sustain a safe and sustainable flight cadence throughout the remainder of the space station’s planned operations.
“Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test-2 went very well and we hope to be able to certify the Starliner system in the near future. However, we will need additional missions from SpaceX to implement our strategy of having each commercial provider flying alternating missions once per year,” said Phil McAllister, director, commercial space at NASA. “Our goal has always been to have multiple providers for crewed transportation to the space station. SpaceX has been reliably flying two NASA crewed missions per year, and now we must backfill those flights to help safely meet the agency’s long-term needs.”
NASA anticipates a potential need to use any additional SpaceX flights as early as 2026 to ensure dissimilar redundancy, maintain safe space station operations, and allow each company to work through any unforeseen issues that could arise as private industry builds operational experience with these new systems.
“The recent success of Boeing’s uncrewed flight test is helping to solidify NASA’s long-term goals,” said Steve Stich, manager, NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. “It’s critical we complete Starliner’s development without undue schedule pressure while working to position both Boeing and SpaceX for sustainable operations in the years ahead.”
SpaceX is currently NASA’s only certified commercial crew transportation provider. The company will fly its sixth rotational mission for NASA in the spring of 2023.
In October 2021, NASA issued a request for information from American industry capable of providing safe, reliable, and cost-effective human space transportation services to and from the International Space Station to ensure a continuous human presence aboard the microgravity laboratory. In February 2022, NASA awarded a firm fixed-price, indefinite-delivery/indefinite-quantity contract modification for the Crew-7, Crew-8, and Crew-9 missions to SpaceX.
After a thorough review of the long-term capabilities and responses from American industry, NASA’s assessment is that the SpaceX crew transportation system is the only one currently certified to maintain crewed flight to the space station while helping to ensure redundant and backup capabilities through 2030.
The current sole source modification does not preclude NASA from seeking additional contract modifications in the future for additional transportation services as needed.
In 2014, NASA awarded the CCtCap contracts to Boeing and SpaceX through a public-private partnership as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. Under CCtCap, NASA certifies that a provider’s space transportation system meets the agency’s requirements prior to flying missions with astronauts. After years of development, commercial crew systems have achieved or are nearing operational readiness for regular crewed missions, including providing a lifeboat capability, to the space station.
NASA’s Psyche spacecraft is nearing the final stages of preparations for launch, and the mission team is working to confirm that all hardware and software systems are operating correctly. An issue is preventing confirmation that the software controlling the spacecraft is functioning as planned. The team is working to identify and correct the issue. To allow more time for this work, the launch period is being updated to no earlier than Sept. 20, 2022, pending range availability.
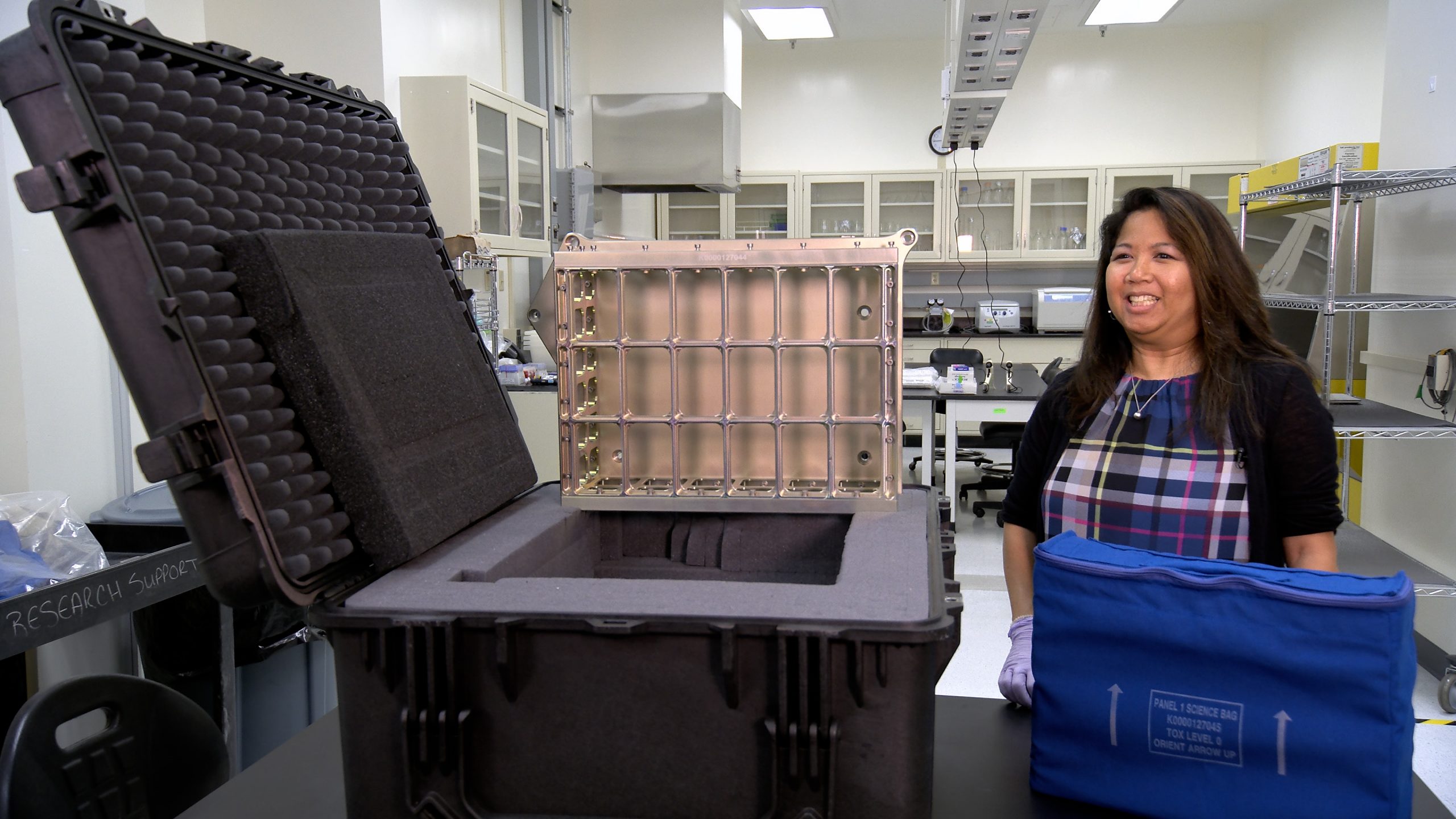
As NASA prepares to return to the Moon through Artemis, teams at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida are working to send much smaller life forms to space to help scientists better understand the effects of space radiation before humans return to the lunar surface.
A number of science experiments, including the agency’s Biology Experiment-1 (BioExpt-1), will be flying on board Artemis I – the mission that will test the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion as an integrated system before sending astronauts to the Moon.
NASA’s Space Biology Program selected four biology experiments to fly as part of BioExpt-1, which involves using plant seeds, fungi, yeast, and algae to study the effects of space radiation before sending humans to the Moon and, eventually, to Mars.
“Each of these four experiments will help us understand a unique aspect of how biological systems can adapt and thrive in deep space,” said Sharmila Bhattacharya, NASA program scientist for space biology. “Gathering information like this and analyzing it after flight will eventually help us paint the full picture of how we can help humans thrive in deep space.”
During Artemis I, Orion will travel more than 40,000 miles beyond the Moon, passing through the Van Allen Belts – areas beyond low-Earth orbit where cosmic radiation is trapped – and providing researchers with a true deep space environment for conducting these experiments.
“We don’t currently know what the effects of radiation are outside of low-Earth orbit and how that could affect our system and our biology,” said Dinah Dimapilis, NASA project manager. “I’m excited to see what we can learn from these experiments, to see us go back to the Moon, and to know that I get to be a part of all of this.”
The four experiments will be split into two science bags fabricated and assembled by personnel with the Test Operations and Support Contract at Kennedy. About three weeks before launch, each science bag will be carefully placed into container assemblies built by a team with the Florida spaceport’s Laboratory Support Services and Operations Contract and then secured to the backbone of Orion.
When Orion finishes its journey and splashes down in the Pacific Ocean, each of the experiments will be returned to the principal investigators for further study. Those principal investigators were awarded grants from NASA Biological and Physical Sciences, totaling approximately $1.6 million. The awardees are Federica Brandizzi, Ph.D., Michigan State University; Timothy Hammond, Ph.D., Institute for Medical Research, Inc.; Zheng Wang, Ph.D., Naval Research Laboratory; and Luis Zea, Ph.D., University of Colorado, Boulder.