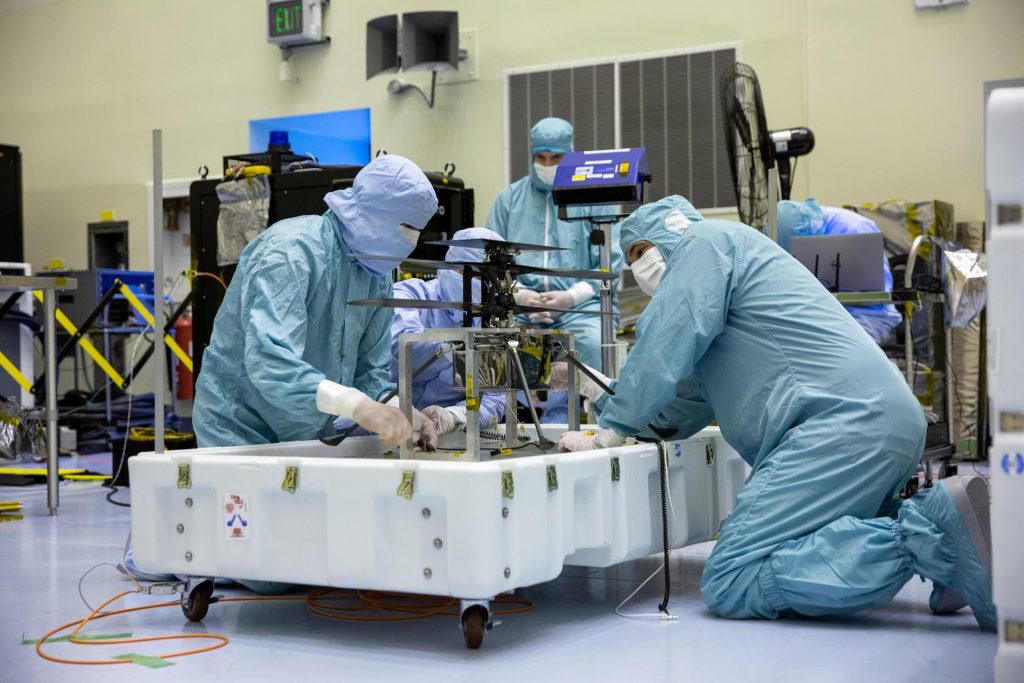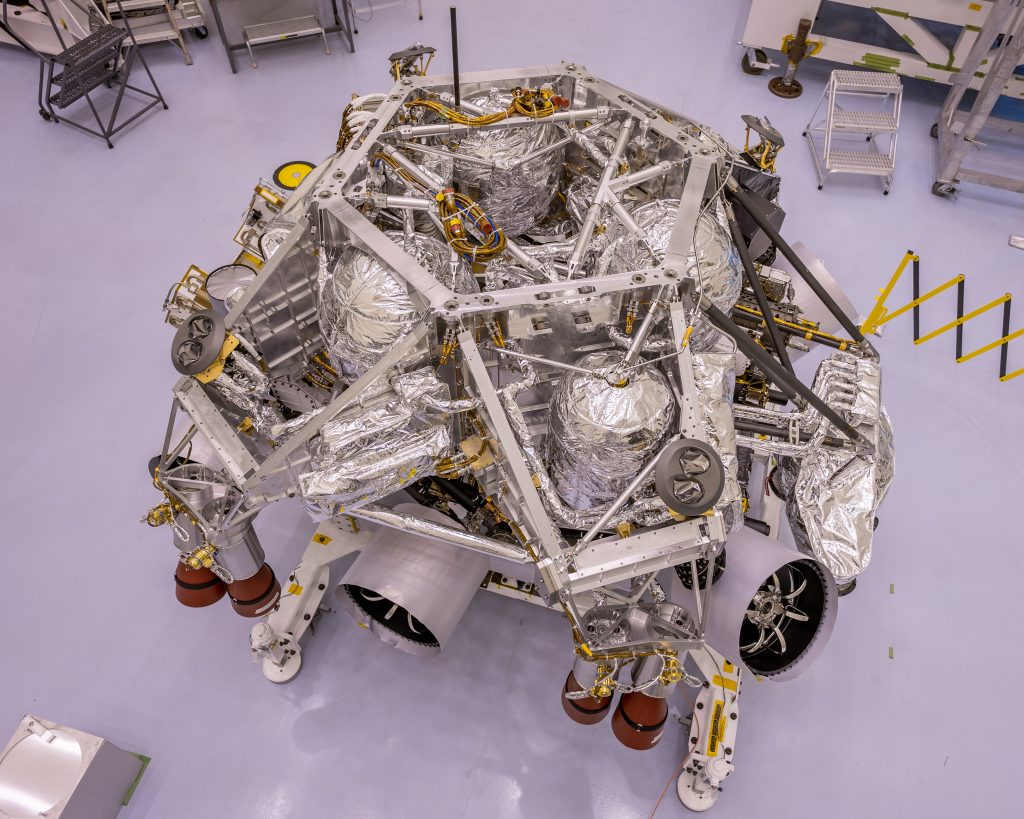
Testing on NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover at Kennedy Space Center closed out April on an extremely high note.
The latest activities at the Florida spaceport included attaching the aeroshell backshell on April 29 and attaching the rover to its rocket-powered descent stage on April 23 inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The rover and descent stage were the first spacecraft components to come together for launch — and they will be the last to separate when the spacecraft reaches Mars on Feb. 18, 2021.
The backshell carries the parachute and several components that will be used during later stages of entry, descent and landing. The aeroshell will encapsulate and protect Perseverance and its descent stage during their deep space journey to Mars and during descent through the Martian atmosphere, which generates intense heat.
April saw other key rover milestones reached at Kennedy. On April 14, the

descent stage — fully loaded with 884 pounds of fuel (a hydrazine monopropellant) — was rotated and spun on two separate measuring fixtures to pinpoint its center of gravity. This will help ensure the descent stage remains stable while guiding Perseverance to a safe landing.
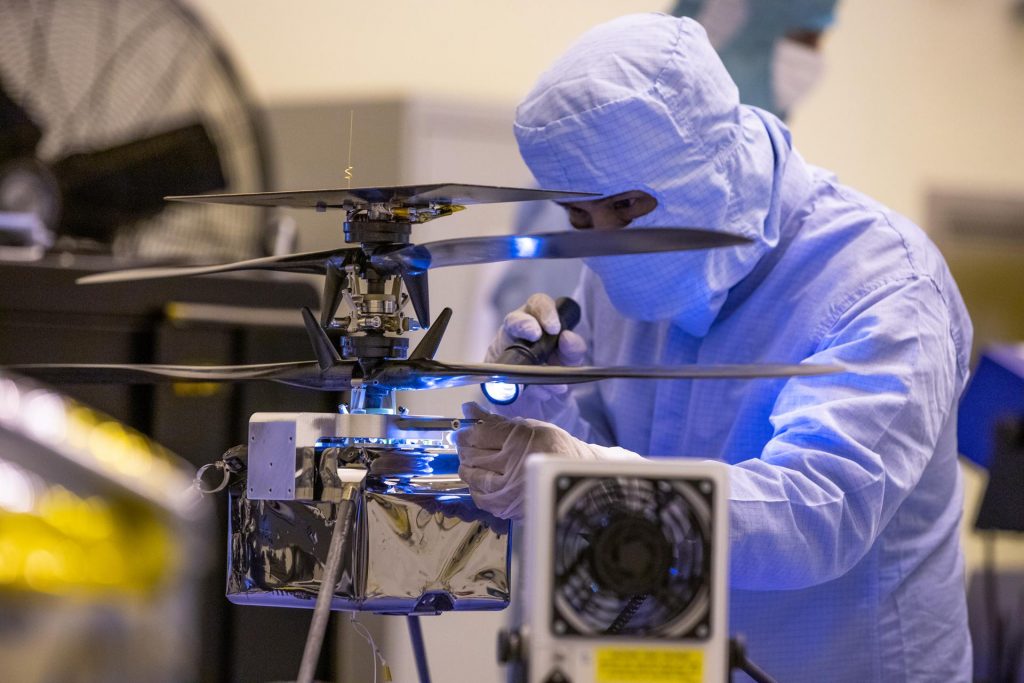
On April 6, NASA’s Mars Helicopter, recently named Ingenuity, was attached to the belly of the rover. Weighing less than four pounds, the twin-rotor, solar-powered helicopter will be released to perform the first in a series of flight tests that will take place during 30 Martian days (a day on Mars is about 40 minutes longer than a day on Earth). Ingenuity will become the first aircraft to fly on another world.
Thanks to the enduring efforts of NASA and United Launch Alliance (ULA) engineers, Perseverance remains on track for its targeted launch period, which opens in just six weeks. The rover will liftoff aboard a ULA Atlas V 541 rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch.
After the rover enters the thin Martian atmosphere, the descent stage will complete the slowing of Perseverance to less than two miles per hour. At about 65 feet over the Martian surface, the descent stage — utilizing a tether of nylon cords — will lower Perseverance to the surface of Jezero Crater. The rover will then sever the cords and the descent stage will fly away.
About the size of a car with dimensions similar to the Curiosity rover, Perseverance will carry seven different scientific instruments. Developed under NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, the rover’s astrobiology mission will search for signs of past microbial life. It will characterize the planet’s climate and geology, collect samples for future return to Earth, and pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet.
Visit the mission website for more information.