Editor’s note: This blog was updated on Feb. 12, 2025, to add the target launch time.
NASA and SpaceX are accelerating the target launch and return dates for the upcoming crew rotation missions to and from the International Space Station. The agency’s Crew-10 launch now is targeting 7:48 p.m. EDT, Wednesday, March 12, pending mission readiness and completion of the agency’s certification of flight readiness process. The Crew-9 mission is planned for return to Earth following a several day handover period with the newly arrived Crew-10 expedition crew.
The earlier launch opportunity is available following a decision by mission management to adjust the agency’s original plan to fly a new Dragon spacecraft for the Crew-10 mission that requires additional processing time. The flight now will use a previously flown Dragon, called Endurance, and joint teams are working to complete assessments of the spacecraft’s previously flown hardware to ensure it meets the agency’s Commercial Crew Program safety and certification requirements. Teams will work to complete Dragon’s refurbishment and ready the spacecraft for flight, which includes trunk stack, propellant load, and transportation to SpaceX’s hangar at 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to be mated with the mission’s Falcon 9 rocket. This will be the fourth mission to the station for this Dragon, which previously supported the agency’s Crew-3, Crew-5, and Crew-7 flights.
“Human spaceflight is full of unexpected challenges. Our operational flexibility is enabled by the tremendous partnership between NASA and SpaceX and the agility SpaceX continues to demonstrate to safely meet the agency’s emerging needs,” said Steve Stich, manager, NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. “We greatly benefit from SpaceX’s commercial efforts and their proactive approach in having another spacecraft ready for us to assess and use in support of Crew-10.”
The change also will allow SpaceX, which owns and operates the Dragon fleet, to complete the new spacecraft’s interior build and perform final integration activities, while simultaneously launching Crew-10 and returning Crew-9 sooner.
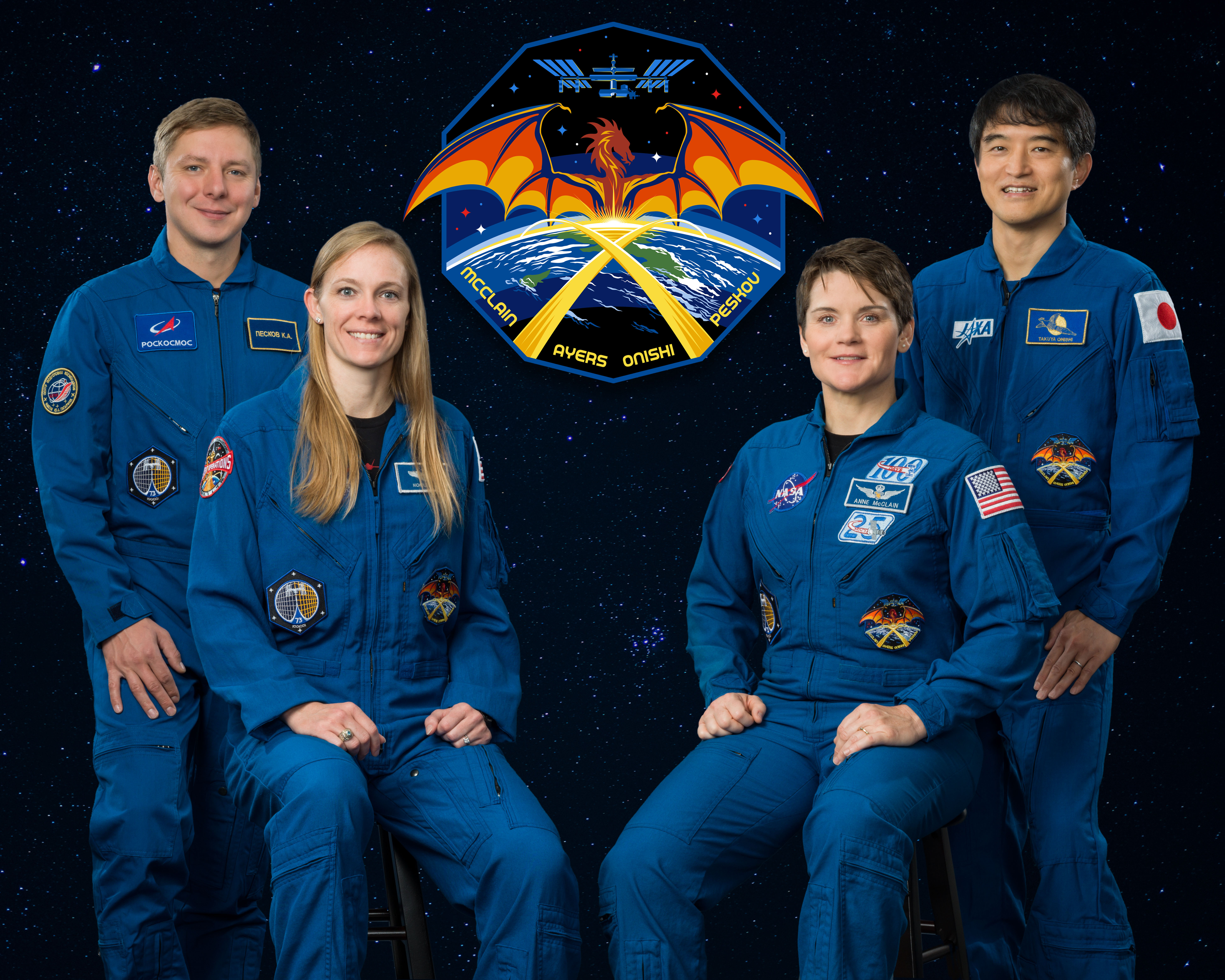
The Crew-10 mission will carry NASA astronauts Anne McClain, commander; and Nichole Ayers, pilot; JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) astronaut Takuya Onishi, mission specialist; and Roscosmos cosmonaut Kirill Peskov, mission specialist, to the space station.
After Crew-10 arrives to the space station, Crew-9 will help the newly arrived crew familiarize with ongoing science and station maintenance work, which supports a safer transition of operations aboard the orbital complex. Following the handover, NASA and SpaceX will prepare to return to Earth NASA astronauts Nick Hague, Suni Williams, and Butch Wilmore, along with Roscosmos cosmonaut Aleksandr Gorbunov aboard Crew-9 pending weather conditions at the splashdown sites off the coast of Florida.