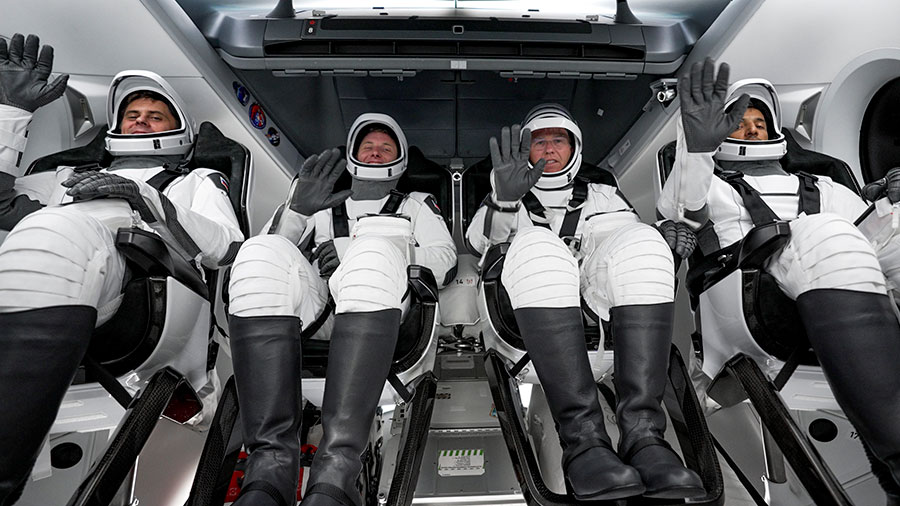
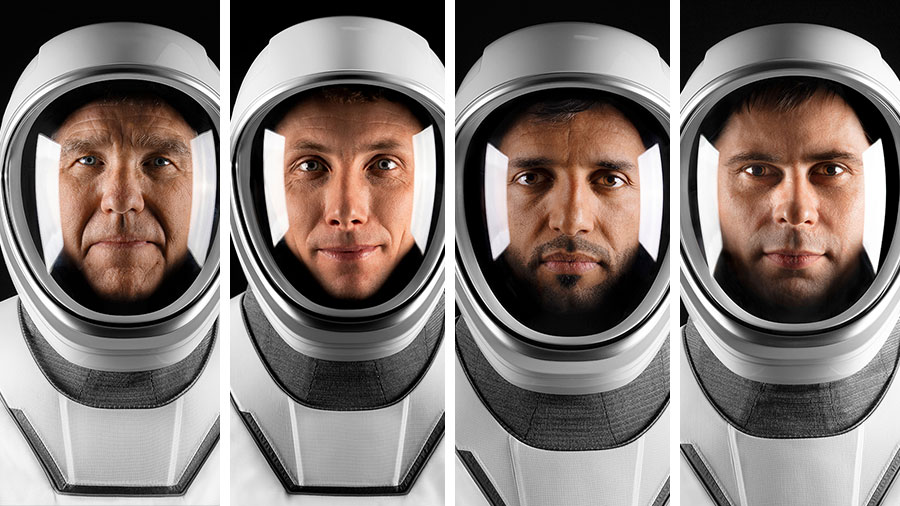
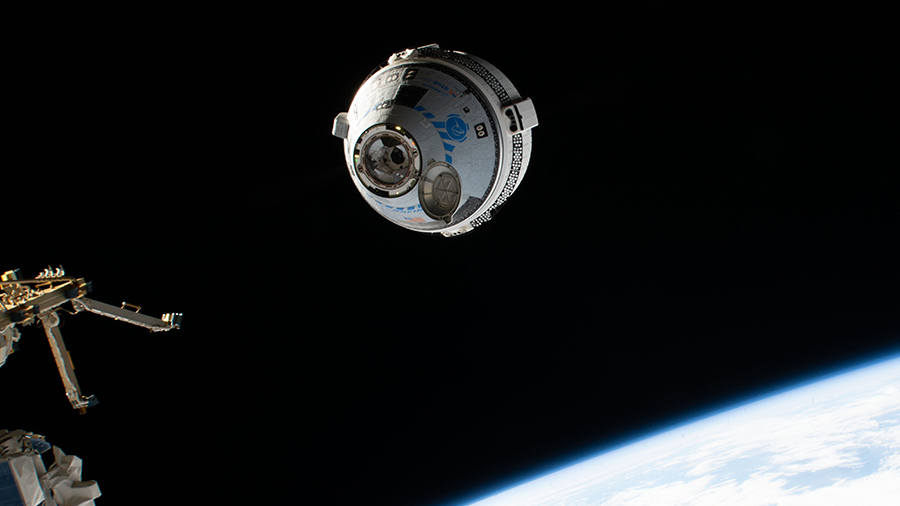
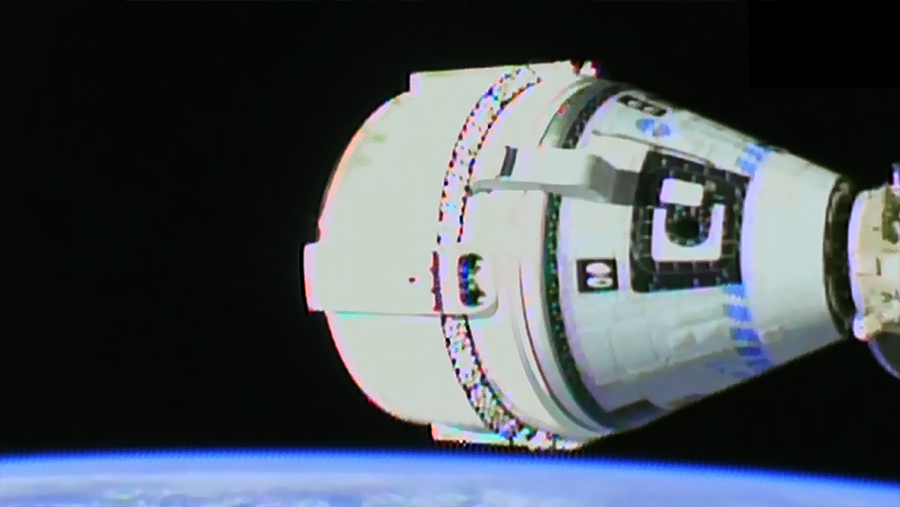
NASA astronauts Stephen Bowen and Woody Hoburg, along with UAE (United Arab Emirates) astronaut Sultan Alneyadi, and Roscosmos cosmonaut Andrey Fedyaev arrived at the International Space Station on Friday, as the SpaceX Dragon, named Endeavour, docked to the complex at 1:40 a.m. EST while the station was 260 statute miles over the Indian Ocean off the east coast of Somalia.
Docking was delayed slightly as mission teams completed troubleshooting of a faulty docking hook sensor on Dragon. The NASA and SpaceX teams verified that all of the docking hooks were in the proper configuration, and SpaceX developed a software override for the faulty sensor that allowed the docking process to successfully continue.
Following Dragon’s link up to the Harmony module, the astronauts aboard the Dragon and the space station will begin conducting standard leak checks and pressurization between the spacecraft in preparation for hatch opening scheduled for 3:18 a.m.
Crew-6 will join the Expedition 68 crew of NASA astronauts Frank Rubio, Nicole Mann, and Josh Cassada, as well as Koichi Wakata of JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency), and Roscosmos cosmonauts Sergey Prokopyev, Dmitri Petelin, and Anna Kikina. For a short time, the number of crew on the space station will increase to 11 people until Crew-5 departs.
NASA Television and the agency’s website are continuing to provide live continuous coverage of the agency’s SpaceX Crew-6 mission.
More details about the Crew-6 mission can be found by following the Crew-6 blog, the commercial crew blog, @commercial_crew on Twitter, and commercial crew on Facebook.
Learn more about station activities by following the space station blog, @space_station and @ISS_Research on Twitter, as well as the ISS Facebook and ISS Instagram accounts.
Get weekly video highlights at: https://roundupreads.jsc.nasa.gov/videupdate/
Get the latest from NASA delivered every week. Subscribe here: www.nasa.gov/subscribe