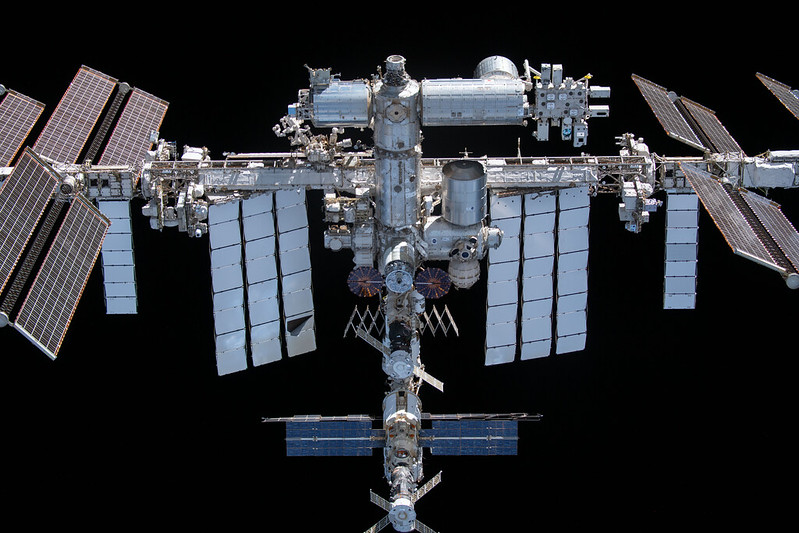
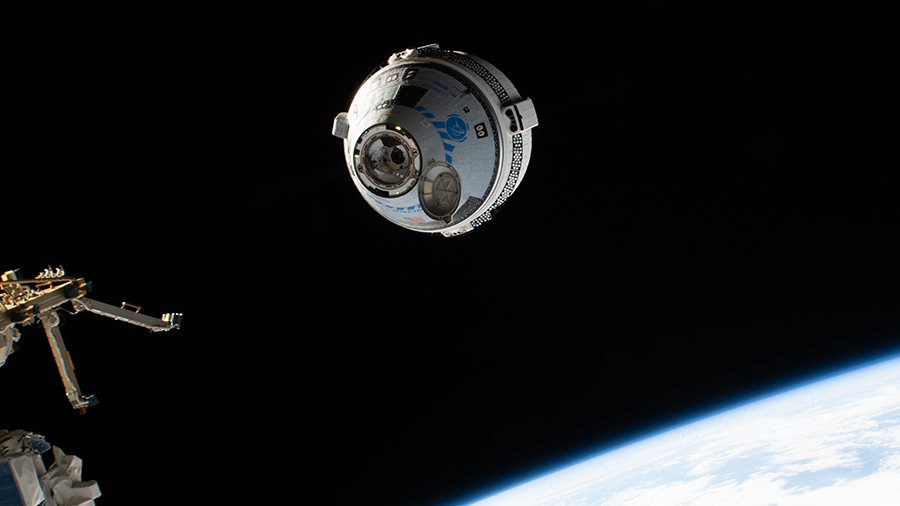
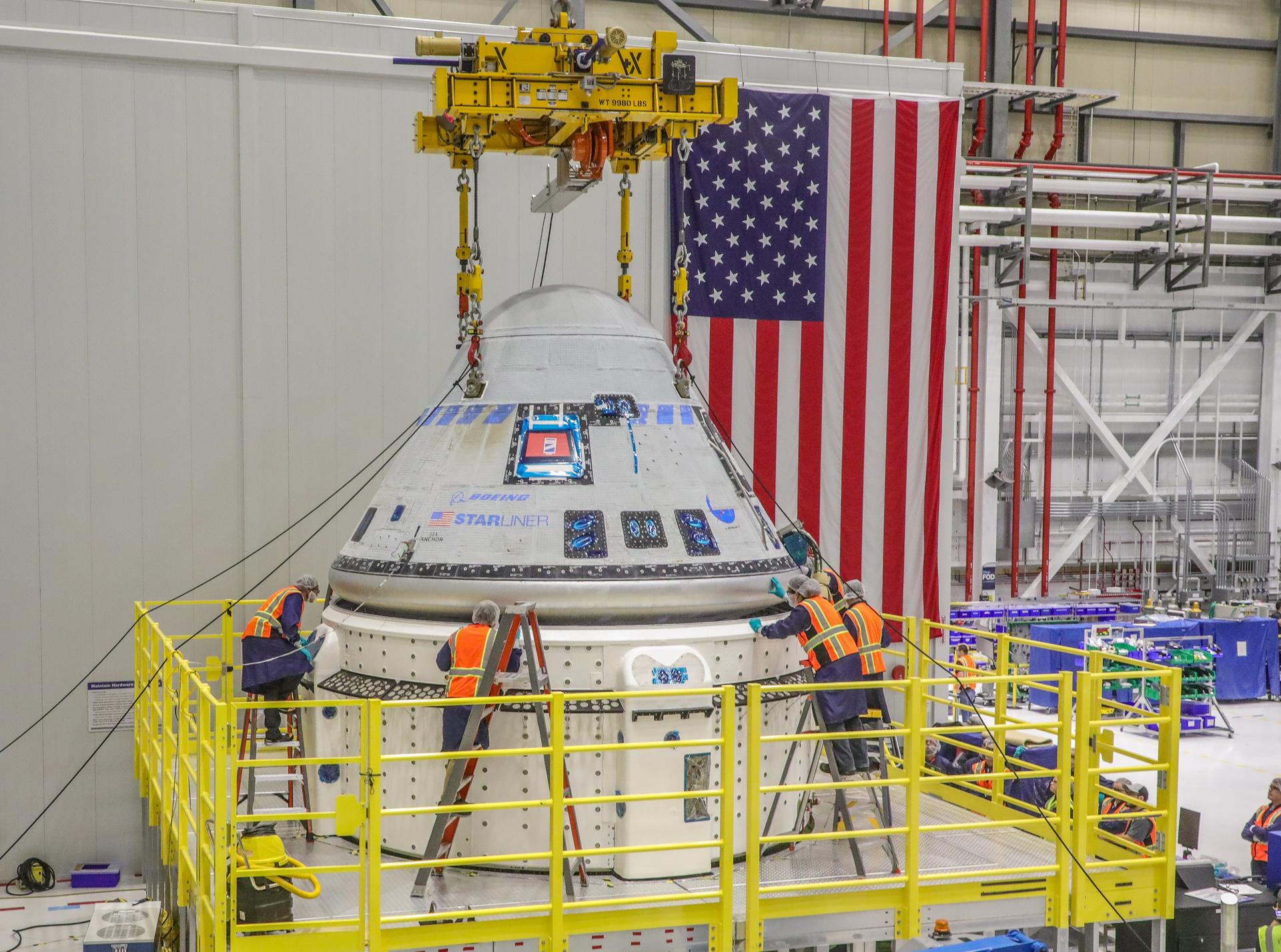
NASA and its industry partners Boeing and SpaceX are planning for the next set of missions to the International Space Station for the agency’s Commercial Crew Program.
Crew-8
NASA’s SpaceX Crew-8 mission to the orbiting laboratory is targeted to launch no earlier than mid-February. The mission will carry NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick, commander; Michael Barratt, pilot; and mission specialist Jeanette Epps, as well as Roscosmos cosmonaut mission specialist Alexander Grebenkin to the space station to conduct a wide range of operational and research activities. Routine maintenance and processing of the Crew-8 SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon spacecraft is in work. This will be the first spaceflight for Dominick, Epps, and Grebenkin, and the third for Barratt. Crew-8 is expected to return to Earth in late August 2024, following a short handover with the agency’s Crew-9 mission.
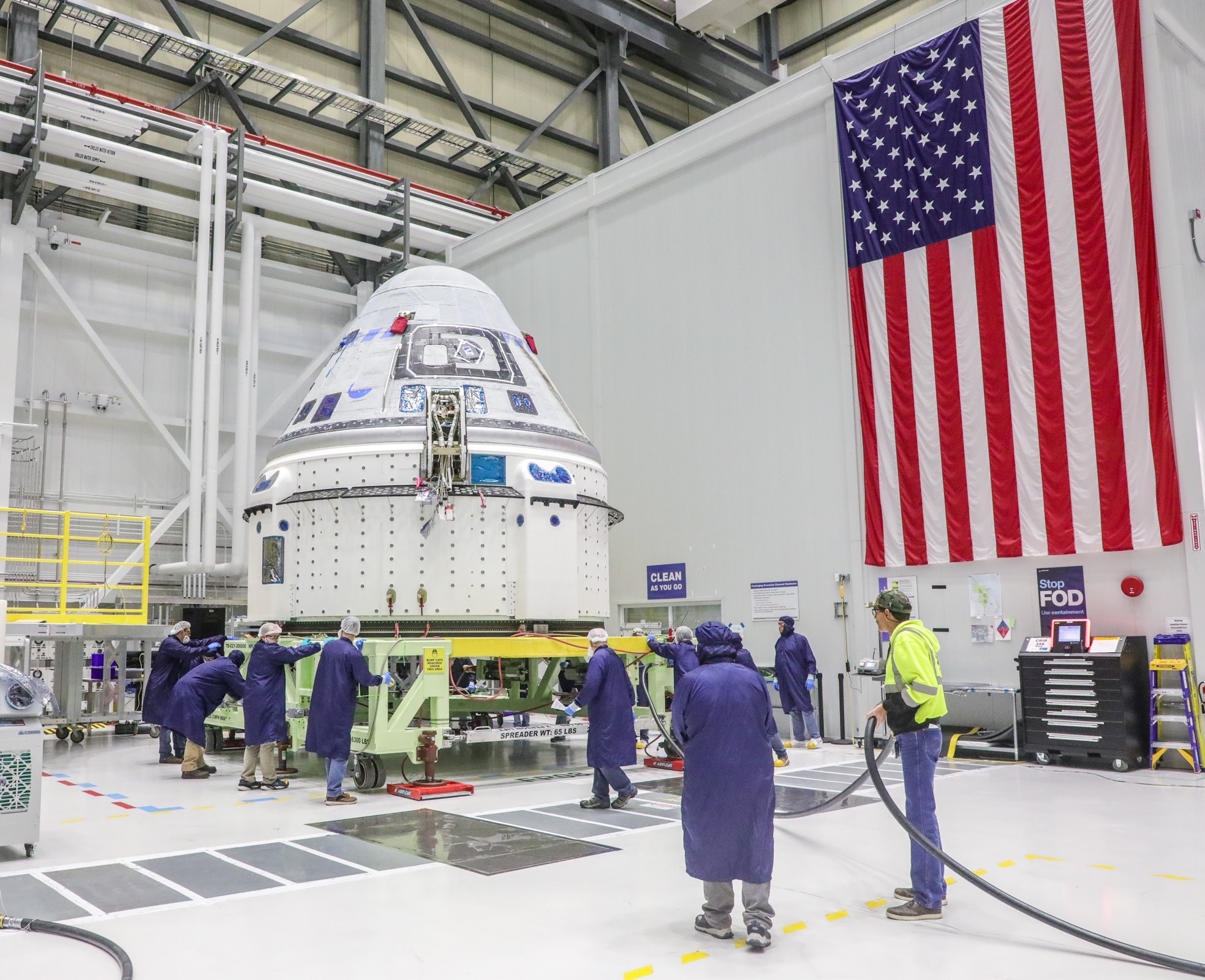
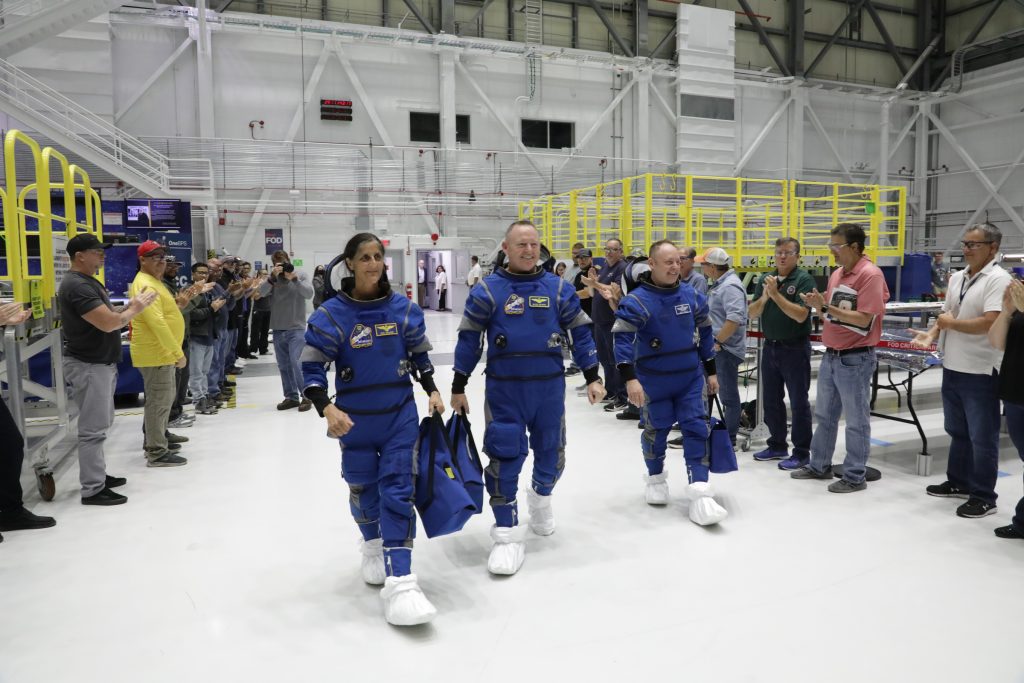
Starliner Crew Flight Test (CFT)
The first crewed flight of the Starliner spacecraft, named NASA’s Boeing Crew Flight Test (CFT), is planned for no earlier than mid-April. CFT will send NASA astronauts and test pilots Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams on a demonstration flight to prove the end-to-end capabilities of the Starliner system. Starliner will launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida, spend approximately eight days docked to the space station, and return to Earth with a parachute and airbag-assisted ground landing in the desert of the western United States.
NASA will provide an updated status of CFT readiness as more information becomes available.
Crew-9
Looking further ahead in 2024, NASA and SpaceX are targeting no earlier than mid-August for the launch of the agency’s Crew-9, SpaceX’s ninth crew rotation mission to the space station for NASA. A crew of four will be announced at a later date.
10th Crew Rotation Mission
The 10th commercial crew rotation opportunity to the space station is targeted for early 2025. NASA is planning for either SpaceX’s Crew-10 or Boeing’s Starliner-1 mission in this slot. The Starliner-1 date was adjusted to allow for the post-flight review of the Crew Flight Test and incorporation of anticipated learning, approvals of final certification products, and completion of readiness and certification reviews ahead of that mission.
For more insight on NASA’s Commercial Crew Program missions to the orbiting laboratory follow the commercial crew blog. More details can be found @commercial_crew on X and commercial crew on Facebook.